Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


(E)-Ferulic acid ((E)-Coniferic acid) causes the phosphorylation of β-catenin, resulting in proteasomal degradation of β-catenin and increases the expression of pro-apoptotic factor Bax and decreases the expression of pro-survival factor survivin.t(E)-Ferulic acid exert both anti-proliferation and anti-migration effects in the human lung cancer cell line H1299.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 45.00 |


| Description | (E)-Ferulic acid ((E)-Coniferic acid) causes the phosphorylation of β-catenin, resulting in proteasomal degradation of β-catenin and increases the expression of pro-apoptotic factor Bax and decreases the expression of pro-survival factor survivin.t(E)-Ferulic acid exert both anti-proliferation and anti-migration effects in the human lung cancer cell line H1299. |
| In vitro | trans-Ferulic acid exerted potent antioxidant effects. However, trans-Ferulic acid increased intracellular ROS levels, including hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion, in H1299 cells. trans-Ferulic acid treatment inhibited cellular proliferation and induced moderate apoptotic cell death at the highest concentration used (0.6 mM). Furthermore, trans-Ferulic acid moderately inhibited the migration of H1299 cells at the concentrations of 0.3 and 0.6 mM and attenuated MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. trans-Ferulic acid caused the phosphorylation of β-catenin, resulting in proteasomal degradation of β-catenin. Conversely, trans-Ferulic acid treatment increased the expression of pro-apoptotic factor Bax and decreased the expression of pro-survival factor survivin. |
| Cell Research | The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay was used to determine free radical scavenging capability. Assessment of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) was evaluated using oxidized 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate and dihydroethidium staining. Trypan blue exclusion, colony formation, and anchorage-independent growth assays were used to determine cellular proliferation. Annexin V staining assay was used to assess cellular apoptosis by flow cytometry. Wound healing and Boyden's well assays were used to detect the migration and invasion of cells. Gelatin zymography was used to detect matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and MMP-9) activity. Western blotting was used to detect expression levels of various signaling pathway proteins. |
| Source |
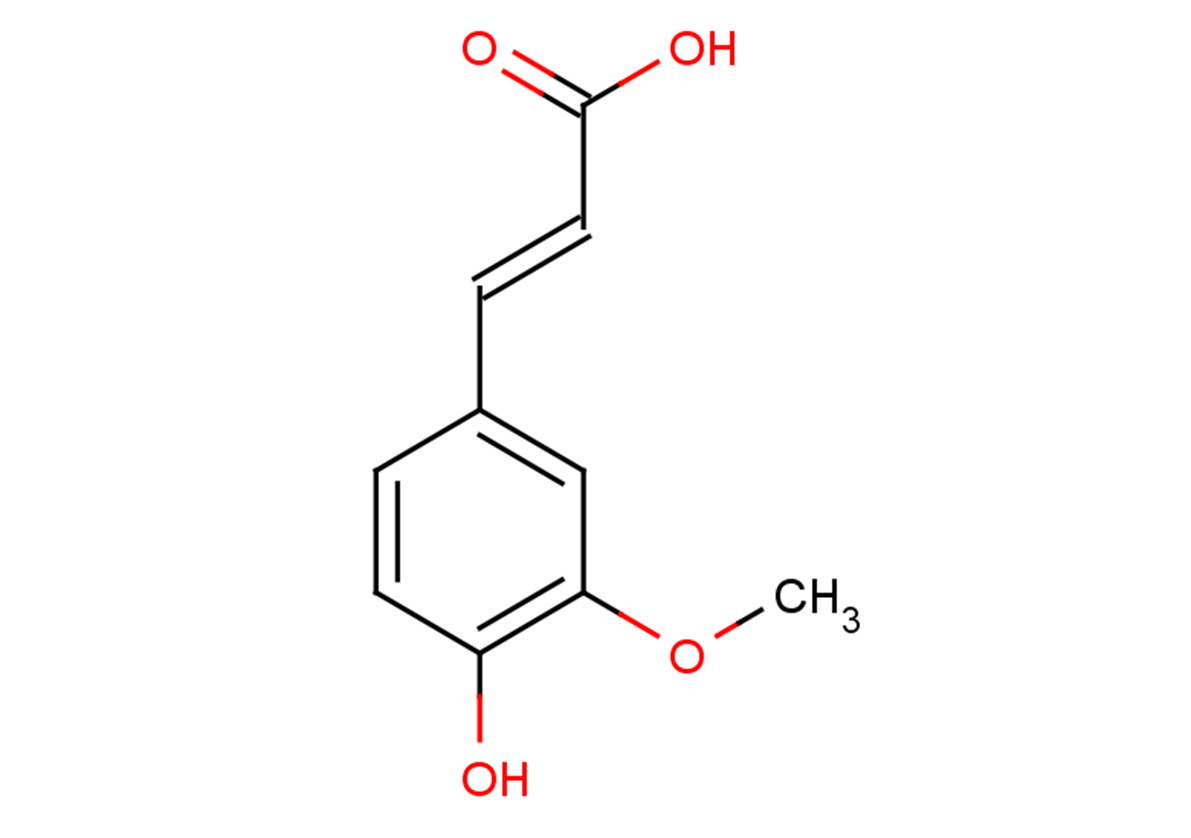
| Synonyms | trans-Ferulic acid, (E)-Coniferic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 194.18 |
| Formula | C10H10O4 |
| CAS No. | 537-98-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 65 mg/mL (334.74 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
(E)-Ferulic acid 537-98-4 Apoptosis Cytoskeletal Signaling Metabolism Stem Cells BCL Ferroptosis Endogenous Metabolite Wnt/beta-catenin Beta catenin trans-Ferulic acid Inhibitor (E) Ferulic acid Bcl-2 Family (E)Ferulic acid Coniferic acid β-catenin Ferulic acid inhibit (E)-Coniferic acid inhibitor
