Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


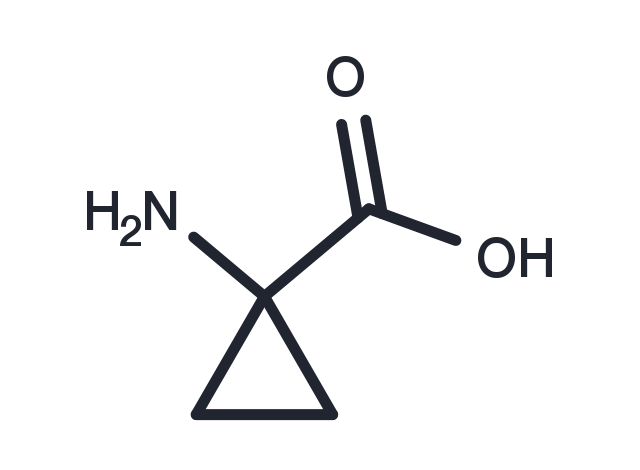
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is an intermediate in the synthesis of ethylene, the plant hormone responsible for biological processes ranging from seed germination to organ senescence. It is a small molecule agonist at the glycine modulatory site of the NMDA receptor (EC50 = 0.7-0.9 μM) in the presence of low levels (1 μM) of glutamate and as a competitive antagonist at the glutamate-binding site on NMDA receptors (EC50 = 81.6 nM) with high levels (10 μM) of glutamate.2 This compound has been reported to protect against neuron cell death in vivo models of ischemia by enabling moderate levels of NMDA receptor activation and attenuating any excess NMDA receptor signaling that may lead to neurotoxicity.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 46.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in H2O) | In stock | $ 48.00 |



| Description | 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is an intermediate in the synthesis of ethylene, the plant hormone responsible for biological processes ranging from seed germination to organ senescence. It is a small molecule agonist at the glycine modulatory site of the NMDA receptor (EC50 = 0.7-0.9 μM) in the presence of low levels (1 μM) of glutamate and as a competitive antagonist at the glutamate-binding site on NMDA receptors (EC50 = 81.6 nM) with high levels (10 μM) of glutamate.2 This compound has been reported to protect against neuron cell death in vivo models of ischemia by enabling moderate levels of NMDA receptor activation and attenuating any excess NMDA receptor signaling that may lead to neurotoxicity. |
| Targets&IC50 | NMDAR:0.7-0.9 µM (EC50) |
| In vivo | The extracellular DA metabolite 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride (3-MT) induces significant behavioral activation in DDD mice. This activity, however, is mostly presented as a set of disorganized abnormal movements that include tremor, head bobbing, straub tail, grooming and abnormal orofacial movements rather than normal forward activity. No effect is observed when 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride is infused at doses below 9 μg, at 9 μg and higher doses 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride dose-dependently causes transient behavioral activation with a complex set of behaviors. In particular, transient hyperactivity and stereotypy, sniffing, grooming, rearing and mild abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) at the level of limbs is observed after infusion of 9 μg of 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride. Similar behaviors are also observed after 18 μg of 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride with the additional appearance of tremor as well as oral and whole body AIMs[1]. |
| Synonyms | 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid, 1-Amino-1-carboxycyclopropane, ACC |
| Molecular Weight | 101.1 |
| Formula | C4H7NO2 |
| CAS No. | 22059-21-8 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 10 mM
DMSO: Insoluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid 22059-21-8 Metabolism Neuroscience Endogenous Metabolite NMDAR 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid 1 Aminocyclopropane 1 carboxylic acid 1Aminocyclopropane1carboxylic acid inhibit 1-Amino-1-carboxycyclopropane ACC Inhibitor inhibitor
