Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


AGN 196996 is a potent and selective inhibitor of RARα (Ki: 2 nM).AGN 196996 has very low affinity for RARβ and RARγ, with a Ki of 1087 nM and 8523 nM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 97.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 263.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 395.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 659.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 939.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 1,280.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 278.00 |

| Description | AGN 196996 is a potent and selective inhibitor of RARα (Ki: 2 nM).AGN 196996 has very low affinity for RARβ and RARγ, with a Ki of 1087 nM and 8523 nM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | RARβ:1087 nM(Ki), RARα:2 nM(Ki), RARγ:8523 nM(Ki) |
| In vitro | AGN 196996 is a potent and selective RARα antagonist with a Ki value of 2 nM; little binding affinity for RARβ(Ki=1087 nM) and RARγ(Ki=8523 nM). RARα antagonist AGN 196996 shows no activity in transactivation assays but instead blocks the gene transcriptional activity induced by ATRA and other RAR agonists.[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 482.32 |
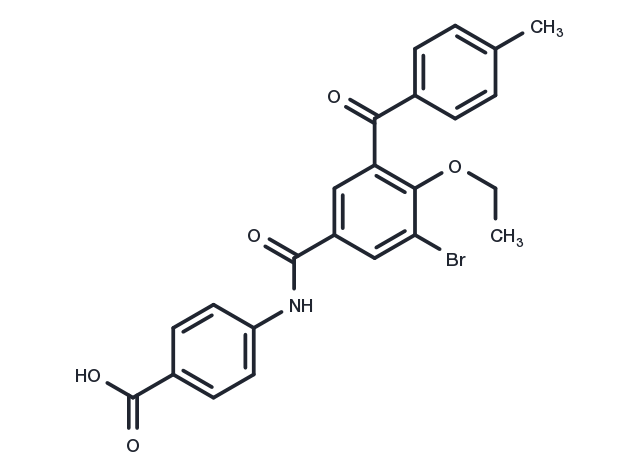
| Formula | C24H20BrNO5 |
| CAS No. | 958295-17-5 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 225.0 mg/mL (466.5 mM), Sonification is recommended.
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
AGN 196996 958295-17-5 Autophagy Metabolism Others Retinoid Receptor AGN196996 AGN-196996 inhibitor inhibit
