Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Agnuside (chasteberry oil) inhibits COX-2 (IC50: 0.026 mg/ml) but exhibits less than 10% inhibition of COX-1 at this concentration. It also inhibits 46.3, 66.8, and 82.1% of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) ATPase activity at concentrations of 5, 25, and 100 μM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 39.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 98.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 148.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 249.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 369.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 548.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 110.00 |




| Description | Agnuside (chasteberry oil) inhibits COX-2 (IC50: 0.026 mg/ml) but exhibits less than 10% inhibition of COX-1 at this concentration. It also inhibits 46.3, 66.8, and 82.1% of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) ATPase activity at concentrations of 5, 25, and 100 μM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | COX-2:0.026 mg/mL |
| In vitro | Agnuside (0.1-10 μM) induces proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells, an effect that is inhibited by the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant [2]. |
| In vivo | Agnuside (50 mg/kg) reduces acetic acid-induced writhing in mice indicating analgesia.3 It also suppresses production of the pro-inflammatory mediators' prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and leukotriene B4 and the T cell-mediated cytokines IL-2, TNF-α, INF-γ, IL-4, IL-10, and IL-17 in splenocytes and arthritic paw tissue from arthritic adrenalectomized rats.4 |
| Source |
| Synonyms | chasteberry oil |
| Molecular Weight | 466.44 |
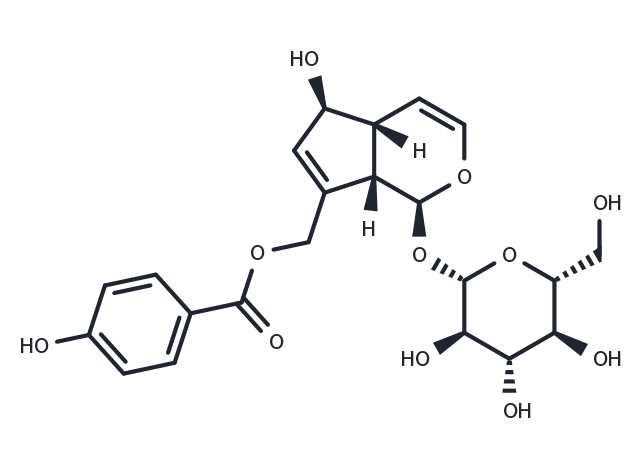
| Formula | C22H26O11 |
| CAS No. | 11027-63-7 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 10 mg/mL
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Agnuside 11027-63-7 GPCR/G Protein Immunology/Inflammation Membrane transporter/Ion channel Neuroscience COX Prostaglandin Receptor P-gp Agnoside Inhibitor inhibit chasteberry oil inhibitor
