Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Amenamevir (ASP2151) is a novel helicase-primase inhibitor that is active against varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (EC50: 14 ng/mL).
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 55.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 126.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 207.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 343.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 531.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 768.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 1,580.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 143.00 |




| Description | Amenamevir (ASP2151) is a novel helicase-primase inhibitor that is active against varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (EC50: 14 ng/mL). |
| Targets&IC50 | Helicase-primase:14 ng/mL |
| In vitro | The mean EC50s of Amenamevir against HSV-1 and HSV-2 are 14 (range, 7.7-20) and 30 ng/mL (range, 15-58), respectively, while those of acyclovir (ACV) is 29 (range, 18-38) and 71 ng/mL (range, 45-95), respectively. |
| In vivo | Amenamevir (ASP2151, 3-30 mg/kg/day) dose-dependently accelerates the reduction in virus titer. Amenamevir dose-dependently decreases both HSV-1 titers and lesion scores, irrespective of the dosing interval. Based on the correlation curves, HSV-1 growth is completely inhibited by Amenamevir (p.o.), and these PK parameters are estimated: Cmax in serum, 10,000 ng/mL or higher; AUC24h, 60 μg ? h/ml or higher; 21 to 24 h for T> 100. The mean concentration of Amenamevir in plasma at 5 days postinfection dose-dependently increases, with doses of 3 mg Amenamevir/g or higher significantly reducing the intradermal HSV-1 titer. |
| Cell Research | The antiviral activities of Amenamevir and ACV against HSVs are tested using a plaque reduction assay. Briefly, HEF cells are seeded into multi-well plates and incubated until they form a monolayer. After the medium is removed, the cells are infected with HSV-1 or HSV-2, and the plates are further incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The cells are washed twice with maintenance medium and then treated with the test compound (including Amenamevir) until clear plaques appear. The cells are then fixed with 10% formalin in phosphate-buffered saline, stained with a 0.02% crystal violet solution, and the number of plaques is determined under a light microscope. The EC50, which represents the concentration of test compound needed to reduce the plaque number by 50%, is calculated using nonlinear regression analysis with a sigmoid-maximum effect (Emax) model[1]. |
| Animal Research | Female hairless mice (HOS: HR-1, 7 to 8 weeks old) are infected with a suspension of HSV-1 strain WT51 (15 μL/mouse; titer, 2×108 PFU/mL) or CI-116 (15 μL/mouse; titer, 4×107 PFU/mL) in the dorsolateral skin stripped as a small square using a needle, under anesthesia. The day of HSV-1 infection is designated day zero postinfection. Total daily doses of 1, 3, 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day ASP2151 are orally administered to HSV-1-infected mice (n=5) for 5 days. Amenamevir (ASP2151) treatments are started 2 to 3 h after HSV infection either as a single daily dose (every 24 h, q24h) or as two (every 12 h, q12h) or three (every 8 h, q8h) divided doses. Lesion scores and intradermal HSV-1 titers are measured on day 5 postinfection[1]. |
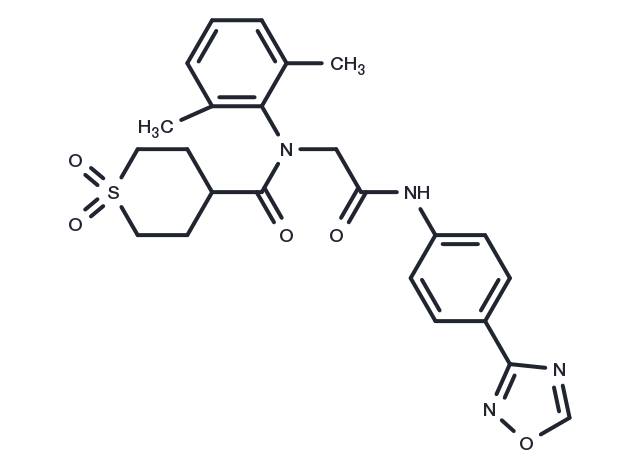
| Synonyms | ASP2151 |
| Molecular Weight | 482.55 |
| Formula | C24H26N4O5S |
| CAS No. | 841301-32-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 160 mg/mL
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Amenamevir 841301-32-4 Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair Microbiology/Virology DNA/RNA Synthesis HSV ASP2151 Herpes simplex virus Inhibitor ASP-2151 ASP 2151 inhibit inhibitor
