Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


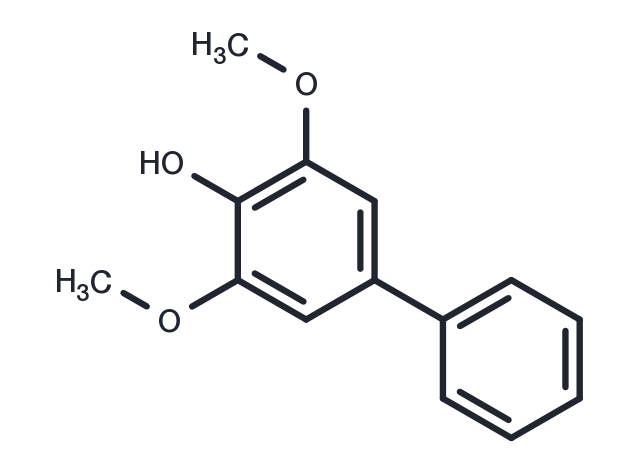
Aucuparin (2,6-dimethoxy-4-phenylphenol) is a plant antibiotic with anti-inflammatory activity. Aucuparin inhibited pulmonary fibrosis in mouse models induced by bleomycin (BLM). ABTS and FRAP showed clear scavenging activity. Aucuparin inhibited superoxide production of human neutrophils induced by fmlp, and its IC50 was 17.0μM.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 538.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 1,070.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 1,430.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 2,130.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 2,880.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 3,880.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 993.00 |

| Description | Aucuparin (2,6-dimethoxy-4-phenylphenol) is a plant antibiotic with anti-inflammatory activity. Aucuparin inhibited pulmonary fibrosis in mouse models induced by bleomycin (BLM). ABTS and FRAP showed clear scavenging activity. Aucuparin inhibited superoxide production of human neutrophils induced by fmlp, and its IC50 was 17.0μM. |
| In vitro |
The formation of Aucuparin, a well-known biphenyl, is induced by yeast extract (YE) in cell cultures of Sorbus aucuparia. Here we demonstrate that the addition of YE to the cell cultures results in a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS; H(2)O(2) and O(2) (-)), followed by transcriptional activation of the biphenyl synthase 1 gene (BIS1) encoding the key enzyme of the biphenyl biosynthetic pathway and Aucuparin accumulation. When the cell cultures were pretreated with superoxide dismutase specific inhibitor N,N-diethyldithiocarbamic acid, although O(2) (-) continued to be generated, the H(2)O(2) accumulation, BIS1 expression, and Aucuparin production were blocked. Interestingly, an exogenous supply of H(2)O(2) in the range of 0.05-10 mM failed to induce Aucuparin accumulation. These results indicate that endogenous generation of H(2)O(2) rather than that of O(2) (-) is a key factor in YE-induced accumulation of biphenyl phytoalexins in cell cultures of S. aucuparia.[1] |
| In vivo | Aucuparin, a natural product isolated from Sorbus aucuparia, inhibited pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin (BLM)-induced lung fibrosis mouse model. In the lung samples of mice treated with aucuparin, the gene expression of inflammation and macrophage activation markers was reduced compared to those treated with BLM alone. Moreover, aucuparin decreased the expression of profibrotic marker genes and increased the expression of antifibrotic marker genes. Finally, we observed that aucuparin significantly suppressed transforming growth factor-β-induced activation of inflammatory cytokine production and collagen synthesis from macrophages and fibroblasts, respectively. [3] |
| Source |
| Synonyms | 2,6-dimethoxy-4-phenylphenol |
| Molecular Weight | 230.26 |
| Formula | C14H14O3 |
| CAS No. | 3687-28-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 2.3 mg/mL (13.2 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Aucuparin 3687-28-3 Immunology/Inflammation NADPH-oxidase 2,6-dimethoxy-4-phenylphenol inhibitor inhibit
