Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


B-AP15 (NSC-687852)(NSC-687852) is a selective inhibitor of the deubiquitinating enzymes Usp14 and UCHL5 of the 26S proteasome. It blocks the deubiquitinating activity of the 26S proteasome.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 32.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 52.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 89.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 133.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 225.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 397.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 676.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 44.00 |






| Description | B-AP15 (NSC-687852)(NSC-687852) is a selective inhibitor of the deubiquitinating enzymes Usp14 and UCHL5 of the 26S proteasome. It blocks the deubiquitinating activity of the 26S proteasome. |
| Targets&IC50 | UCHL5:2.1 μM |
| In vitro | In mice with HCT-116 colon carcinoma xenografts, B-AP15 (5 mg/kg) significantly delayed tumor onset. Additionally, in severely immunodeficient mice bearing squamous cell carcinoma xenografts, B-AP15 (5 mg/kg) demonstrated notable antitumor activity. |
| In vivo | As a UPS (Ubiquitin-Proteasome System) inhibitor, B-AP15 induces cell death by triggering the cathepsin-D-dependent lysosomal apoptotic pathway. Compared to peripheral blood mononuclear cells or immortalized epithelial cells (hTERT-RPE1), B-AP15 exhibits greater cytotoxicity towards HCT-116 cells. It dose-dependently accumulates the UbG76V-YFP receptor (IC50: 0.8 μM), indicating impaired proteasomal degradation. When applied to human colon cancer HCT-116 cells, B-AP15 (1 μM) rapidly accumulates polyubiquitinated proteins. At a concentration of 1 μM, B-AP15 inhibits the release of IL-1β induced by ATP from lipopolysaccharide-induced peritoneal macrophages. In THP-1 cells, 1 μM B-AP15 reduces the level of cell death induced by nigericin and significantly decreases the formation of ASC specks in lipopolysaccharide-induced THP-1 cells treated with nigericin. Additionally, B-AP15 (1 μM) causes a G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and accumulation of cell cycle inhibitors in HCT-116 cells. At 2.2 μM, B-AP15 dose-dependently increases the levels of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors CDKN1A and CDKN1B, and the tumor suppressor gene TP53, without affecting the levels of ornithine decarboxylase 1. |
| Kinase Assay | For deubiquitinase inhibition assays, 19S regulatory particle (5 nM), 26S (5 nM) UCH-L1 (5 nM), UCH-L3 (0.3 nM), USP2CD (5 nM) USP7CD (5 nM) USP8CD (5 nM) or BAP1 (5 nM) is incubated with DMSO or b-AP15 and monitored the cleavage of ubiquitin-AMC (1,000 nM) using a Wallac VICTOR Multilabel counter or a Tecan Infinite M1000 equipped with 380 nm excitation and 460 nm emission filters[1]. |
| Cell Research | b-AP15 is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use[2]. Cell viability is monitored by either the fluorometric microculture cytotoxicity assay or the MTT assay. For the MTT assay, cells are seeded into 96-well flat-bottomed plates overnight and exposed to drugs, using DMSO as the control. At the end of incubations, 10 μl of a stock solution of 5 mg/mL MTT is added into each well, and the plates are incubated 4 hours at 37°C. Formazan crystals are dissolved with 100 μL 10% SDS/10 mM HCl solution overnight at 37°C. Absorbance is measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate reader at 590 nm[2]. |
| Synonyms | NSC 687852 |
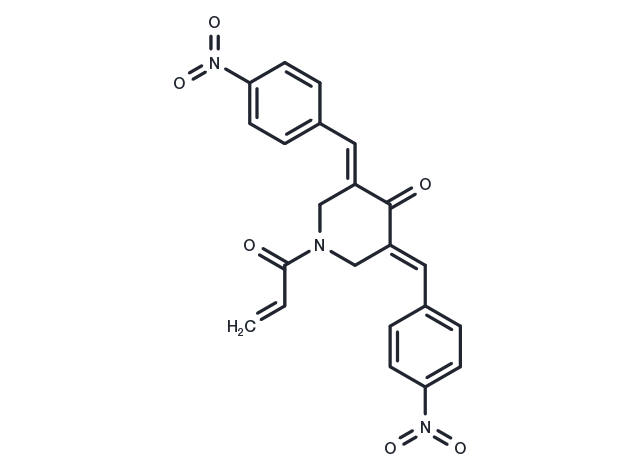
| Molecular Weight | 419.39 |
| Formula | C22H17N3O6 |
| CAS No. | 1009817-63-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 41.9 mg/mL (100 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
B-AP15 1009817-63-3 Apoptosis Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair Ubiquitination DUB Deubiquitinase Inhibitor BAP15 inhibit NSC-687852 DUBs B AP15 NSC 687852 b-AP15 B-AP-15 NSC687852 inhibitor
