Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Benzyl benzoate (Benzoic acid benzyl ester) is one of the older preparations used for the therapy of scabies. Scabies is a skin infection caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei. Its symptoms are red spots, severe itching (particularly at night), and may lead to a secondary infection. Benzyl benzoate is useful in the therapy of scabies because it is lethal to this mite. It is also used for the therapy of lice affection of the body and head. Benzyl benzoate is not the therapy of choice for scabies because of its irritant properties.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 33.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 47.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 66.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 106.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 39.00 |



| Description | Benzyl benzoate (Benzoic acid benzyl ester) is one of the older preparations used for the therapy of scabies. Scabies is a skin infection caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei. Its symptoms are red spots, severe itching (particularly at night), and may lead to a secondary infection. Benzyl benzoate is useful in the therapy of scabies because it is lethal to this mite. It is also used for the therapy of lice affection of the body and head. Benzyl benzoate is not the therapy of choice for scabies because of its irritant properties. |
| In vitro | Benzyl benzoate possess oestrogenic activity in MCF7 human breast cancer cells in vitro. It is able to increase the growth of oestrogen-dependent MCF7 human breast cancer cells[1]. |
| Cell Research | Cells are added to the required volume of phenol red-free RPMI 1640 medium containing 5% DCFCS at a concentration of about 0.2 × 105 cells ml−1 and plated in monolayer in 0.5 ml aliquots into 24-well plastic tissue culture dishes (Nunc). After 24 h, the medium is changed to the same medium but containing the required concentration of test compound. Culture medium is changed routinely every 3–4 days. Cell counts are performed by counting released nuclei on a model ZBI Coulter Counter. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Ascabiol, Novoscabin, Scabitox, Benzoic acid benzyl ester |
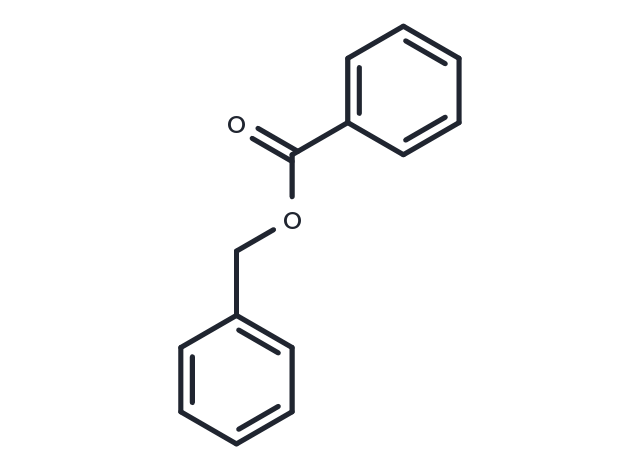
| Molecular Weight | 212.24 |
| Formula | C14H12O2 |
| CAS No. | 120-51-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 50 mg/mL (235.58 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Benzyl benzoate 120-51-4 Microbiology/Virology Parasite Ascabiol Benzyl inhibit Inhibitor Novoscabin Scabitox Benzyl Benzoate Benzoic acid benzyl ester inhibitor
