Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Cilazapril Monohydrate (Justor) is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 4-6weeks | $ 58.00 | |
| 10 mg | 4-6weeks | $ 94.00 | |
| 25 mg | 4-6weeks | $ 198.00 | |
| 50 mg | 4-6weeks | $ 347.00 | |
| 100 mg | 4-6weeks | $ 648.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | 4-6weeks | $ 81.00 |
| Description | Cilazapril Monohydrate (Justor) is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. |
| In vitro | BML-190 has 50-fold selectivity for CB2 receptors over CB1 receptors. In HEK-293 cells stably expressing the human CB2 receptor, BML-190 potentiates the forskolin-stimulated accumulation of cAMP. BML-190 reduces the basal levels of inositol phosphate production in cells expressing the CB2 receptor. 10 μM of BML-190 decreases inositol phosphates accumulation by 38%. [1] BML-190 is an aminoalkylindole. BML-190 is found to yield at least 15 metabolic products. [2] BML-190 diminishes LPS-induced NO and IL-6 production in a concentration-dependent manner. BML-190 also inhibits LPS-induced PGE2 production and COX-2 induction. [3] |
| In vivo | Cilazapril (1 mg/kg, daily) tends to decrease and the higher dose (10 mg/kg, daily) significantly decreases systolic blood pressure (SBP) in subtotal nephrectomized rats. Cilazapril attenuates the further development of protein uria in a dose-dependent manner in subtotal nephrectomized rats. Cilazapril attenuates the increase in plasma fibrinogen concentration and serum albumin concentration in a dose-dependent manner. Cilazapril reduces serum MCP-1 concentration in the nephrectomized rats. Cilazapril decreases hepatic fibrinogen synthesis through the alleviation of the local inflammatory process and the improvement of hypoalbuminemia. [1] Cilazapril normalizes systolic arterial pressure to 121 mm Hg (SD) in the treated SHR-SP rats. Cilazapril decreases systolic arterial pressure to a nearly normal level and prevents hypertensive retinal vascular changes, probably by improving endothelial function. [2] Cilazapril results in a marked decrease in the Kd of the renal arginine vasopressin (AVP) receptor and an increase in the plasma AVP level in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. [3] Cilazapril exerts a rapid, complete, and persistent antihypertensive effect in the spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) in vivo but has no effect on SAP in the normotensive Sprague-Dawley rat. Cilazapril treatment depresses heart performance (28-35%) in SHR but has no effect in the Sprague-Dawley rats. [4] Cilazapril decreases blood pressure to control values and reduces HW:BW in hyperthyroid rats. [5] |
| Synonyms | Ro 31-2848 monohydrate, Justor |
| Molecular Weight | 435.51 |
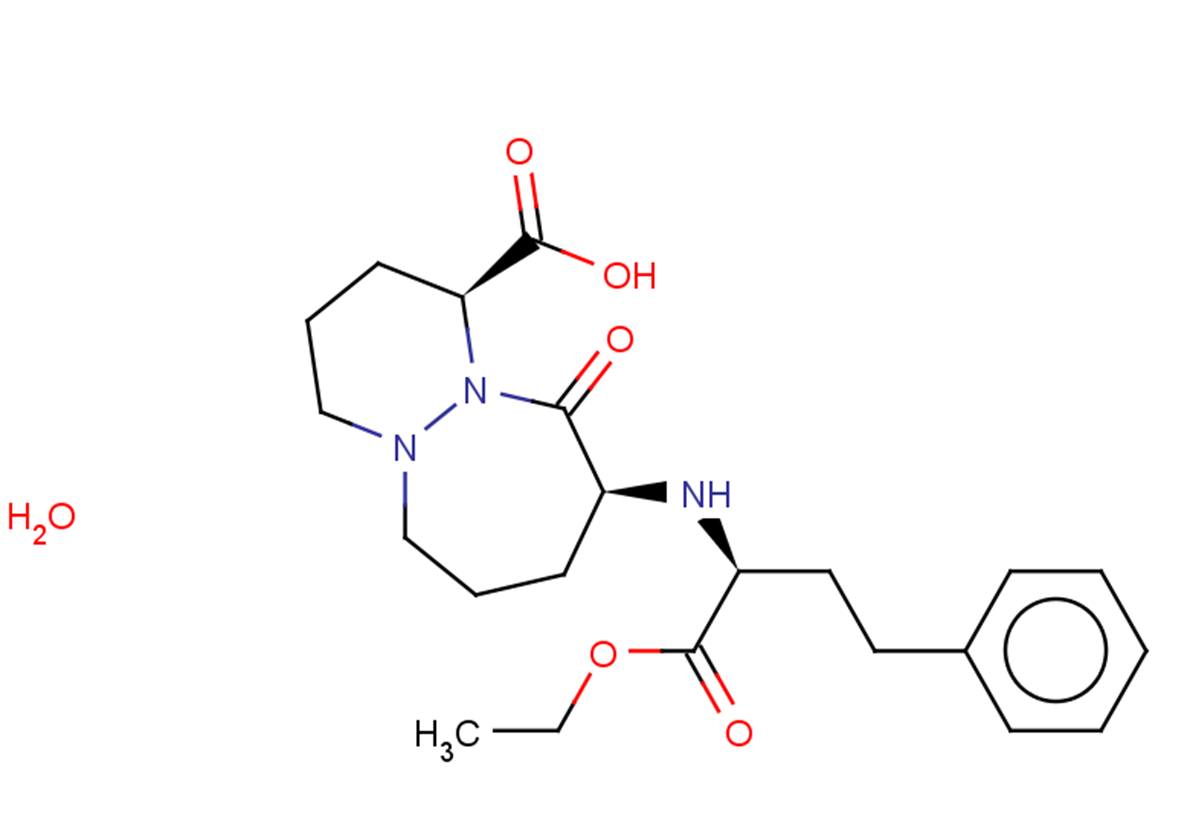
| Formula | C22H31N3O5·H2O |
| CAS No. | 92077-78-6 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Ethanol: 81 mg/mL (186 mM)
H2O: <1 mg/mL
DMSO: 81 mg/mL (186 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Cilazapril Monohydrate 92077-78-6 Endocrinology/Hormones RAAS Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE) Ro 31-2848 monohydrate Justor Inhibitor Ro 31-2848 Monohydrate Ro 31-2848 inhibit Cilazapril inhibitor
