Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Clevudine (Levovir) is a synthetic pyrimidine analogue with activity against hepatitis B virus (HBV). Intracellularly, clevudine is phosphorylated to its active metabolites, clevudine monophosphate and triphosphate. The triphosphate metabolite competes with thymidine for incorporation into viral DNA, thereby causing DNA chain termination and inhibiting the function of HBV DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). Clevudine has a long half-life and shows significant reduction of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), therefore the patient is less likely to have a relapse after treatment is discontinued.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 47.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 128.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 207.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 369.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 80.00 |



| Description | Clevudine (Levovir) is a synthetic pyrimidine analogue with activity against hepatitis B virus (HBV). Intracellularly, clevudine is phosphorylated to its active metabolites, clevudine monophosphate and triphosphate. The triphosphate metabolite competes with thymidine for incorporation into viral DNA, thereby causing DNA chain termination and inhibiting the function of HBV DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). Clevudine has a long half-life and shows significant reduction of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), therefore the patient is less likely to have a relapse after treatment is discontinued. |
| In vitro | Clevudine is a potent antiviral agent against HBV (EC50 0.1 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells) as well as EBV, which has low cytotoxicities in a variety of cell lines including MT2, CEM, H1 and HepG2 2.2.15 and bone marrow progenitor cells. Clevudine is metabolized in cells by the cellular thymidine kinase as well as deoxycytidine kinase to its monophosphate, and subsequently to the di- and triphosphate. Clevudine is known to act specifically on viral DNA synthesis, and its triphosphate inhibits the HBV DNA synthesis in a dose-dependent manner without being incorporated into the DNA or chain termination. [1] Clevudine results in increase of the amounts of the diphosphate and triphosphate metabolites of these analogs. Clevudine monophosphate (L-FMAUMP) is a poorer substrate than its D-configuration anomer. [2] Clevudine is readily phosphorylated to the corresponding 5'-triphosphate form of the compound in cell culture, which involves the mechanism of action of Clevudine. [3] |
| In vivo | Clevudine is a potent antiviral agent against HBV (EC50 0.1 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells) as well as EBV, which has low cytotoxicities in a variety of cell lines including MT2, CEM, H1 and HepG2 2.2.15 and bone marrow progenitor cells. Clevudine is metabolized in cells by the cellular thymidine kinase as well as deoxycytidine kinase to its monophosphate, and subsequently to the di- and triphosphate. Clevudine is known to act specifically on viral DNA synthesis, and its triphosphate inhibits the HBV DNA synthesis in a dose-dependent manner without being incorporated into the DNA or chain termination. [1] Clevudine results in increase of the amounts of the diphosphate and triphosphate metabolites of these analogs. Clevudine monophosphate (L-FMAUMP) is a poorer substrate than its D-configuration anomer. [2] Clevudine is readily phosphorylated to the corresponding 5'-triphosphate form of the compound in cell culture, which involves the mechanism of action of Clevudine. [3] |
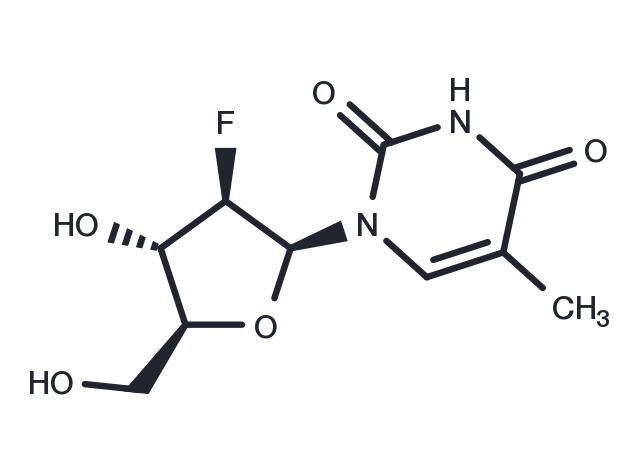
| Synonyms | L-FMAU, Levovir |
| Molecular Weight | 260.22 |
| Formula | C10H13FN2O5 |
| CAS No. | 163252-36-6 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 48 mg/mL (184.5 mM)
DMSO: 49 mg/mL (188.3 mM)
Ethanol: 4 mg/mL (15.37 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Clevudine 163252-36-6 Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair Microbiology/Virology HBV DNA/RNA Synthesis Orthopoxvirus half-life L-FMAU nucleoside analog Inhibitor polymerase Hepatitis B virus low toxicity inhibit Levovir inhibitor
