Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Clindamycin hydrochloride (Clinimycin HCl) inhibits protein synthesis by acting on the 50S ribosomal. It is the hydrochloride salt form of clindamycin, a semi-synthetic, chlorinated broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by chemical modification of lincomycin. Clindamycin hydrochloride(Clinimycin HCl) is used as a solid in capsules.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 40.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 48.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 59.00 | |
| 1 g | In stock | $ 91.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |


| Description | Clindamycin hydrochloride (Clinimycin HCl) inhibits protein synthesis by acting on the 50S ribosomal. It is the hydrochloride salt form of clindamycin, a semi-synthetic, chlorinated broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by chemical modification of lincomycin. Clindamycin hydrochloride(Clinimycin HCl) is used as a solid in capsules. |
| In vitro | Clindamycin is a classical inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis which binds to the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit. [1] |
| In vivo | Clindamycin hydrochloride is rapidly absorbed orally in dogs, exhibiting a mean absorption time (MAT) of 0.87 hours and a bioavailability of 72.55%. It shows a total clearance (CL) rate post intravenous (IV) and oral administration of 0.503 and 0.458 L/h/kg respectively, and reaches a steady-state volume of distribution (IV) of 2.48 L/kg, indicating extensive distribution throughout the body's fluids and tissues. Serum concentrations of clindamycin remain above 0.5 μg/mL for approximately 10 hours after both IV and oral administration. [1] Additionally, it significantly reduces oral malodor, dental plaque, dental calculus, and gingival bleeding in dogs over a period of 42 days. [2] At a dosage of 2.5 mg/lb following ultrasonic scaling, root planing, and polishing (USRP), clindamycin significantly impacts plaque and pocket depth related to periodontal disease, though not gingivitis. [3] Furthermore, it achieves a complete remission ratio of 71.4% (15/21) in dogs with canine superficial bacterial pyoderma within 14 to 28 days. [4] |
| Kinase Assay | In vitro potency assays: After RO4929097 is used, the Aβ peptides are measured by ECL assays using a variety of anti-Aβ antibodies and an Origen 1.5 Analyzer. The 4 g8 murine mAb binds an epitope in the Aβ peptide (within amino acids 18–21) that is immediately distal to the α-secretase cleavage site. The G2–10 murine mAb binds the C terminus that is exposed after γ-secretase-mediated cleavage to generate amino acid 40 of the Aβ40 peptide. The FCA3542 rabbit antibody binds the C terminus that is exposed after γ-secretase-mediated cleavage to generate amino acid 42 of the Aβ42 peptide. The 4 g8 mAb is biotinylated with biotin-LC-sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide-ester. The G2–10 and FCA3542 antibodies are ruthenylated with TAG-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester. Aβ(x-40) is detected with biotinylated 4 g8 and ruthenylated G2–10. Aβ(x-42) is detected with biotinylated 4 g8 and ruthenylated FCA3542. |
| Synonyms | Sobelin HCl, Cleocin, Clindamycin HCl, Clinimycin HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 461.44 |
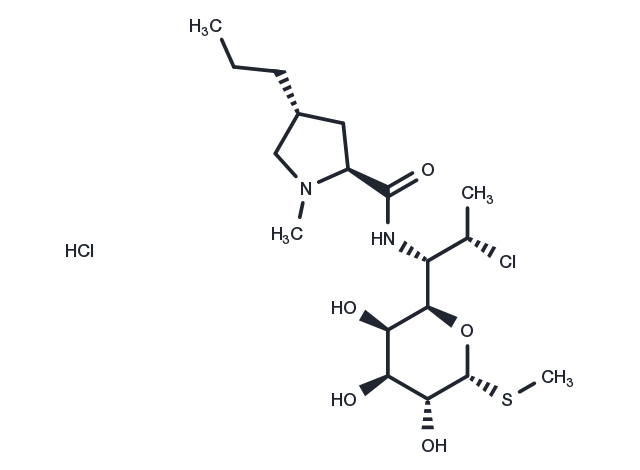
| Formula | C18H33ClN2O5S·HCl |
| CAS No. | 21462-39-5 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 46.1 mg/mL (100 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Clindamycin hydrochloride 21462-39-5 Microbiology/Virology Antibacterial Antibiotic inhibit Inhibitor Clindamycin Sobelin HCl Bacterial Cleocin Clindamycin Hydrochloride Clindamycin HCl Clinimycin HCl inhibitor
