Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Copanlisib dihydrochloride (BAY 80-6946 dihydrochloride) is an ATP-competitive pan-class I PI3K inhibitor (IC50s: 0.5 nM, 0.7 nM, 3.7 nM and 6.4 nM for PI3Kα, PI3Kδ, PI3Kβ and PI3Kγ). Copanlisib dihydrochloride has superior antitumor activity and it also has more than 2,000-fold selectivity against other lipid and protein kinases, except for mTOR.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 47.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 128.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 222.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 372.00 |


| Description | Copanlisib dihydrochloride (BAY 80-6946 dihydrochloride) is an ATP-competitive pan-class I PI3K inhibitor (IC50s: 0.5 nM, 0.7 nM, 3.7 nM and 6.4 nM for PI3Kα, PI3Kδ, PI3Kβ and PI3Kγ). Copanlisib dihydrochloride has superior antitumor activity and it also has more than 2,000-fold selectivity against other lipid and protein kinases, except for mTOR. |
| Targets&IC50 | mTOR:45 nM, PI3Kγ:6.4 nM, PI3Kα:0.5 nM, PI3Kβ:3.7 nM, PI3Kδ:0.7 nM |
| In vitro | In both KPL4 cells and LPA-stimulated PC3 cells, BAY 80-6946 reduces pAKT levels. In a subset of human cancer cell lines with PIK3CA mutations and/or overexpression of HER2, BAY 80-6946 shows antiproliferative activity and induces apoptosis. [1] The combination of HER2-targeted therapies and BAY 80-6946 inhibits growth more effectively than either therapy used alone, and can restore sensitivity to trastuzumab and lapatinib in cells. [2] |
| In vivo | In rat KPL4 or HCT116 tumor xenograft model, BAY 80-6946 (6 mg/kg, i.v.) induces 100% complete tumor regression. In nude mice with Lu7860 erlotinib-resistant, patient-derived NSCLC and MAXF1398 patient-derived luminal breast tumor models, BAY 80-6946 (14 mg/kg, i.v.) also causes tumor growth inhibition. [1] |
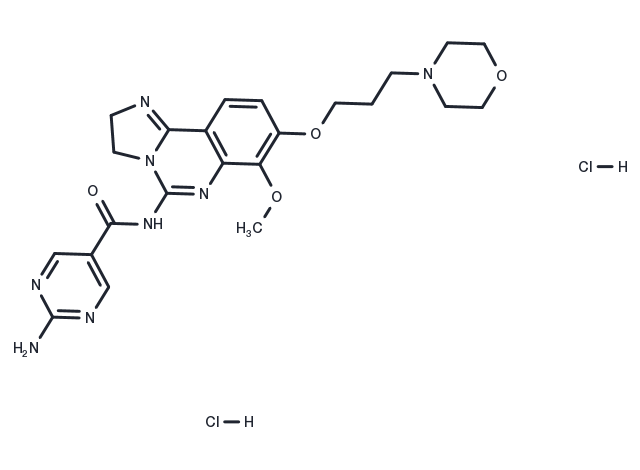
| Synonyms | BAY 80-6946 dihydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 553.44 |
| Formula | C23H30Cl2N8O4 |
| CAS No. | 1402152-13-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 10 mM
H2O: 20 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended.
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Copanlisib dihydrochloride 1402152-13-9 Apoptosis PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling PI3K mTOR Inhibitor antiproliferative inhibit intravenous BAY 80-6946 sub-nanomolar Copanlisib BAY 80-6946 dihydrochloride BAY 80-6946 Dihydrochloride phosphorylation Copanlisib Dihydrochloride Phosphoinositide 3-kinase AKT antitumor administration inhibitor
