Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


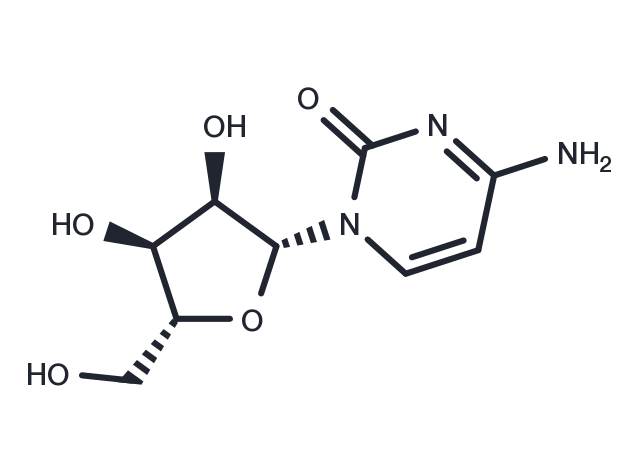
Cytidine (Cytosine-1-β-D-ribofuranoside) is a pyrimidine nucleoside comprised of a cytosine bound to ribose via a beta-N1-glycosidic bond. Cytidine is a precursor for uridine. Both cytidine and uridine are utilized in RNA synthesis.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 46.00 | |
| 1 g | In stock | $ 55.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |



| Description | Cytidine (Cytosine-1-β-D-ribofuranoside) is a pyrimidine nucleoside comprised of a cytosine bound to ribose via a beta-N1-glycosidic bond. Cytidine is a precursor for uridine. Both cytidine and uridine are utilized in RNA synthesis. |
| In vivo | D-cycloserine (DCS) facilitates extinction of conditioned freezing to the light CS when no drug pre-exposure has occurred, but pre-exposure to DCS just prior to conditioning disrupted the facilitation of extinction effect in mice. [1] D-cycloserine (DCS) which has a high affinity for the glycine modulatory site in the NMDA receptor complex modulated memory processing in a dose-dependent manner. DCS also facilitates retention in 'senescence-accelerated mice' in which impairment of learning andmemory increases with age. [2] D-cycloserine (DCS) exhibits facilitated extinction of fear but are able to reacquire fear of that conditioned stimulus (CS) in a similar manner as saline-treated control rats. DCS-treated rats exhibits generalized extinction (i.e., they are less fearful of a non-extinguished CS) in comparison to controls. [3] D-cycloserine (DCS), an antimycobacterial agent known to cross the blood-brain barrier, binds with high affinity to this glycine modulatory site, functions as a positive modulator, and facilitates performance of learningtasks in rats. DCS appears to be a potent cognitive enhancer at doses lower than those required for antibacterial activity. [4] D-cycloserine injections (3.25, 15, or 30 mg/kg) before 30 non-reinforced light exposures dose-dependently enhances extinction but does not influence fear-potentiated startle in rats that does not receive extinction training. [5] |
| Synonyms | Cytosine-1-β-D-ribofuranoside, Cytosine β-D-riboside |
| Molecular Weight | 243.22 |
| Formula | C9H13N3O5 |
| CAS No. | 65-46-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 45 mg/mL (185 mM)
DMSO: 46 mg/mL (189.1 mM)
Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Cytidine 65-46-3 Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair Metabolism Nucleoside Antimetabolite/Analog Endogenous Metabolite RNA nucleoside inhibit Cytosine-1-β-D-ribofuranoside Cytosine b-D-riboside Cytosine-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside Cytosine beta-D-riboside ribofuranose uridine Cytosine β-D-riboside Inhibitor Cytosine-1-b-D-ribofuranoside inhibitor
