Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


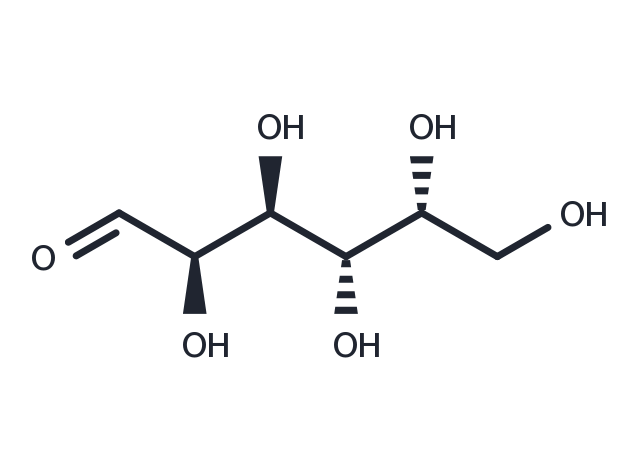
D-Galactose (Alpha-D-galactose) is an aldohexose that exists naturally in the D-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins and is converted enzymatically into D-glucose for metabolism or polysaccharides for storage. It accelerates senescence in invertebrates and mammals and has been used as a model for aging.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 30.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 42.00 | |
| 1 g | In stock | $ 50.00 | |
| 5 g | In stock | $ 68.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |



| Description | D-Galactose (Alpha-D-galactose) is an aldohexose that exists naturally in the D-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins and is converted enzymatically into D-glucose for metabolism or polysaccharides for storage. It accelerates senescence in invertebrates and mammals and has been used as a model for aging. |
| In vitro | Galactose is important for the survival and virulence of bacteria. Galactose is utilized by the Leloir pathway in Escherichia coli. Two anomers of d-galactose are used for different purposes, α-d-galactose as a carbon source and β-d-galactose for induction of UDP-galactose synthesis for biosynthetic glycosylation[1]. |
| In vivo | Chronic D-galactose exposure induces neurodegeneration by enhancing caspase-mediated apoptosis and inhibiting neurogenesis and neuron migration in mice, as well as increasing oxidative damage. Moreover, D-galactose-induced toxicity in mice is a useful model for studying the mechanisms of neurodegeneration and neuroprotective drugs and agents[2]. D-galactose given by oral route leads to cognitive impairments in rats which are accompanied by oxidative damage. Cognitive impairments is observed in the open-field test in the 4th and 6th weeks after d-gal administration, as well as an impairment in spatial memory in the radial maze test after the 6th week of d-gal administration[3]. |
| Synonyms | D-(+)-Galactose, D-Galactopyranose, Alpha-D-galactose |
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
| Formula | C6H12O6 |
| CAS No. | 59-23-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 66mg/mL(366.34mM)
DMSO: 55 mg/mL (305.28 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
D-Galactose 59-23-4 Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite D-(+)-Galactose a-D-galactose inhibit Inhibitor D-Galactopyranose DGalactose α-D-galactose Alpha-D-galactose D Galactose inhibitor
