Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


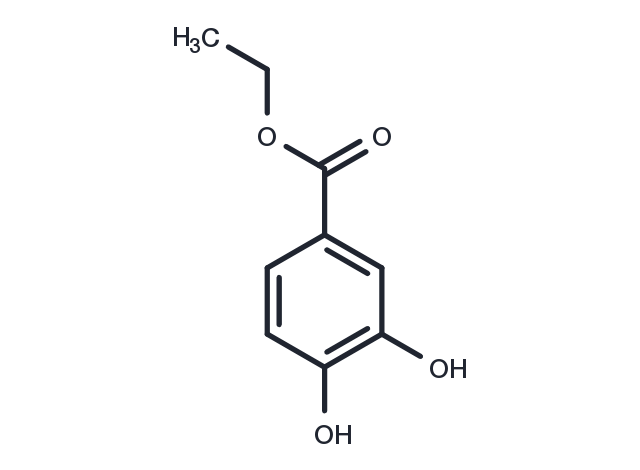
Ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (EDHB): a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor attenuates acute hypobaric hypoxia mediated vascular leakage in brain.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 45.00 |


| Description | Ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (EDHB): a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor attenuates acute hypobaric hypoxia mediated vascular leakage in brain. |
| In vitro | It is shown that DHB reversibly inhibits both morphological and biochemical differentiation of myoblasts, if it is added to the culture medium before the cell alignment stage.Along with the inhibition of procollagen synthesis, DHB also decreases markedly the production of a collagen-binding glycoprotein (gp46) present in the ER[1]. |
| In vivo | EDHB supplementation effectively scaled down HH induced cerebral edema with concomitant downregulation of brain NF-κB expression.?There was significant curtailment of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules.?There was significant downregulation of permeability factor VEGF by EDHB with concomitant increment in hypoxia inducible factor (HIF1α) and anti-inflammatory proteins HO-1 and MT-1 compared to HH control thus accentuating the potential of EDHB as effective hypoxic preconditioning agent in ameliorating HH mediated injury in brain[2]. |
| Animal Research | Male Sprague-Dawley rats treated with EDHB (75 mg/kg for 3 days), were subjected to acute HH exposure at 9144 m (30,000 ft) for 5 h. Animals were assessed for transvascular leakage and edema formation in brain and role of key inflammatory markers along with hypoxia responsive genes. |
| Molecular Weight | 182.17 |
| Formula | C9H10O4 |
| CAS No. | 3943-89-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 22.5 mg/mL (123.51 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate 3943-89-3 Apoptosis Autophagy Chromatin/Epigenetic Immunology/Inflammation Metabolism NF-Κb Others Reactive Oxygen Species NO Synthase HIF/HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase antioxidant ROS NOS Ethyl 3,4 dihydroxybenzoate Hypoxia-inducible factors prolyl-hydroxylase inhibit HIF-PH Ethyl protocatechuate HIFs Ethyl 3,4dihydroxybenzoate Inhibitor collagen Nitric oxide synthases mitochondrial inhibitor
