Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


HA14-1, a Bcl-2/Bcl-XL antagonist, is a non-peptidic ligand of a Bcl-2 surface pocket (IC50: ~9 μM).
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 39.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 62.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 89.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 128.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 30.00 |



| Description | HA14-1, a Bcl-2/Bcl-XL antagonist, is a non-peptidic ligand of a Bcl-2 surface pocket (IC50: ~9 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | BCL2:9 μM |
| In vitro | In immunodeficient mice, HA14-1 (400 nM) does not significantly affect the growth of glioblastomas on its own. However, in vivo, HA14-1 (400 nM) enhances the efficacy of the DNA-damaging agent etoposide (2.5 mg/kg) in inhibiting the growth of glioblastomas. |
| In vivo | When applied to follicular lymphoma cell lines HF1A3, HF4.9, and HF28RA, HA14-1 exhibits cytotoxicity with LC50 values of 4.5/12.6/8.1 μM, respectively. HA14-1 induces apoptosis in HL-60 cells in a dose-dependent manner through the activation of caspases. Moreover, HA14-1 triggers apoptosis in HF4.9, HF1A3, and HF28RA cells through caspase and ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) pathways. |
| Kinase Assay | Affinity determination: The binding affinity of organic compounds to Bcl-2 protein in vitro is determined by a competitive binding assay based on fluorescence polarization. For this assay, 5-carboxyfluorecein is coupled to the N terminus of a peptide, GQVGRQLAIIGDDINR, derived from the BH3 domain of Bak (Flu-BakBH3), which has been shown to bind to the surface pocket of the Bcl-xL protein with high-affinity. According to our molecular modeling studies and binding measurement using fluorescence polarization, the Flu-BakBH3 peptide binds the surface pocket of Bcl-2 with a similar affinity. Bcl-2 used in this assay is a recombinant GST-fused soluble protein. Flu-BakBH3 and Bcl-2 protein are mixed in the presence or absence of organic compounds under standard buffer conditions and are incubated for 30 min. The binding of Flu-BakBH3 to Bcl-2 protein is measured on a LS-50 luminescence spectrometer equipped with polarizers using a dual path length quartz cell (500 μl). The fluorophore is excited with vertical polarized light at 480 nm (excitation slit width 15 nm), and the polarization value of the emitted light is observed through vertical and horizontal polarizers at 530 nm (emission slit width 15 nm). The binding affinity of each compound for Bcl-2 protein is assessed by determining the ability of different concentrations of the compound to inhibit Flu-BakBH3 binding to Bcl-2. |
| Cell Research | The cytotoxic effects of HA14-1 against different FL cell lines are determined by the MTT assay. Briefly, the cells (5000/well) are incubated in triplicate in 96-well plate in the presence or absence of HA14-1 for 20 h at 37 °C. Thereafter, the MTT solution is added to each well. After 4 h incubation at 37 °C, the optical density (OD) is measured by means of 96-well plate reader, with the extraction buffer as a blank. The following formula is used: percentage cell viability = (OD of the experiment samples/OD of the control) × 100. Sigmoidal dose-response curves are fitted to the mean cell viability plotted against log HA14-1 dose and lethal concentration 50% (LC50) values are calculated from the resulting curves using Prism 4.0 softw(Only for Reference) |
| Molecular Weight | 409.23 |
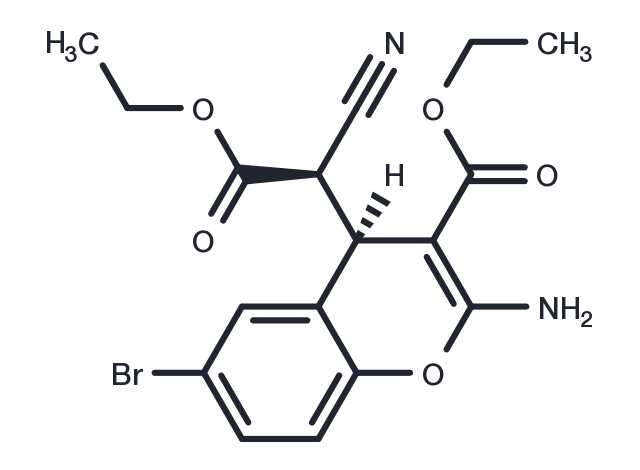
| Formula | C17H17BrN2O5 |
| CAS No. | 65673-63-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Ethanol: 40.9 mg/mL (100 mM)
DMSO: 40.9 mg/mL (100 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
HA14-1 65673-63-4 Apoptosis BCL Bcl-2 Family HA141 HA14 1 HA-14-1 inhibit Inhibitor inhibitor
