Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


LFM-A13(IC50=2.5 μM), a specific Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), is more than 100-fold specificity than other protein kinases, such as JAK1, JAK2, HCK, EGFR, and IRK.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 31.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 47.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 74.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 167.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 283.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 479.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 47.00 |


| Description | LFM-A13(IC50=2.5 μM), a specific Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), is more than 100-fold specificity than other protein kinases, such as JAK1, JAK2, HCK, EGFR, and IRK. |
| Targets&IC50 | BTK:2.5 μM |
| In vitro | In BTK+ B-lineage leukemic cells, LFM-A13 enhances their sensitivity to ceramide- or vincristine-induced apoptosis. [1] In BCL-1 cells, NALM-6 cells, or normal BALB/c splenocytes, LFM-13 inhibits the enzymatic activity of BTK in BCL-1 cells without affecting the BTK protein expression levels [2] In human neutrophils, LFM-A13 decreases the tyrosine phosphorylation induced by fMet-Leu-Phe and inhibits the production of superoxide anions and the stimulation of adhesion, chemotaxis, and phospholipase D activity. [3] |
| In vivo | In BALB/c mice bearing BCL-1 leukemia, combination of LFM-A13 (50 mg/kg/day i.p.) and the standard triple-drug VPL prolongs the median survival time. [2] In primary myeloma-bearing SCID-rab mice, LFM-A13 inhibits osteoclast activity, prevents myeloma-induced bone resorption and suppresss myeloma growth. [4] |
| Molecular Weight | 360 |
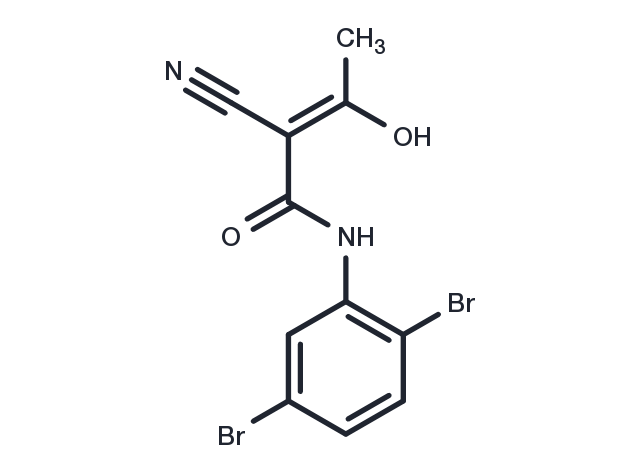
| Formula | C11H8Br2N2O2 |
| CAS No. | 244240-24-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 67 mg/mL (186.1 mM)
H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
LFM-A13 244240-24-2 Angiogenesis Cell Cycle/Checkpoint Chromatin/Epigenetic JAK/STAT signaling Stem Cells Tyrosine Kinase/Adaptors PLK JAK BTK Janus kinase LFM-A-13 Inhibitor LFMA13 Polo-like Kinase (PLK) Bruton tyrosine kinase Btk LFM A13 inhibit inhibitor
