Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Naringin dihydrochalcone (Naringin DC) is an inhibitor of CYP enzymes, used as an artificial sweetener.
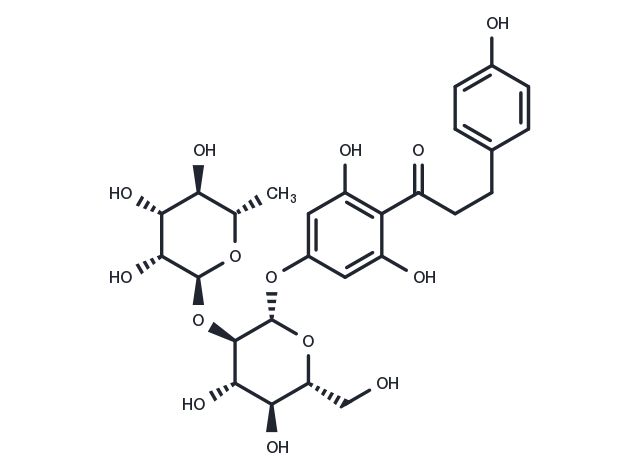
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 42.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 46.00 |


| Description | Naringin dihydrochalcone (Naringin DC) is an inhibitor of CYP enzymes, used as an artificial sweetener. |
| In vitro | Naringin Dihydrochalcone(Naringin DC) is a new-style sweetening agent and an artificial sweetener derived from naringin, a bitter compound found in citrus. [1] It is 500-700 times sweeter than sucrose. Due to its many advantages like high sweet taste, low caloric, innocuity and safety, it can be used in edible, medicine and commodity trade. And because it tastes cleanlily, has long aftertaste and special faint scent and owns fine virtue of shielding bitterness, Naringin DC is in particular used for milky goods, fattiness and grease, freezed foodstuff, machining vegetable, jelly, comfiture, nonalcohol beverage, chewing gum, toothpaste and troche. Besides, it can substitute sugar for decreasing body absorption to sugar. It is really a evangel for fat person and patients who can not eat sugar. |
| In vivo | Treatment with naringin significantly mitigates renal injury in diabetic rats, while also substantially boosting their body weight. Additionally, naringin administration notably reduces collagen deposition and renal interstitial fibrosis. This treatment is associated with decreased levels of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) and MDA (Malondialdehyde), alongside enhanced activities of SOD (Superoxide Dismutase) and GSH-Px (Glutathione Peroxidase)[2]. Oral administration of naringin markedly improves cognitive functions, specifically learning and memory abilities. Furthermore, it substantially strengthens the insulin signaling pathway[3]. |
| Cell Research | HBZY-1 cells are plated into 96-well plates and pretreated with various concentrations(1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 μM) of naringin for 2 h. Then cells are treated with 30 mM glucose for 24 h. The control group is added sterile normal saline in the same volume. After treatment, all the wells are incubated with 20 μl of 5 mg/ml MTT for 4 h at 37°C. Subsequently, 100 μl of DMSO are used to dissolve the formed formazan crystals after removal of the supernatant. The result is recorded at 490 nm on a microplate reader[1]. |
| Source |
| Synonyms | Naringin DC |
| Molecular Weight | 582.55 |
| Formula | C27H34O14 |
| CAS No. | 18916-17-1 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
Ethanol: 93 mg/mL (159.6 mM)
DMSO: 93 mg/mL (159.6 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Naringin dihydrochalcone 18916-17-1 Metabolism NF-Κb P450 NF-κB Naringin DC Inhibitor Nuclear factor-κB Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibit inhibitor
