Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


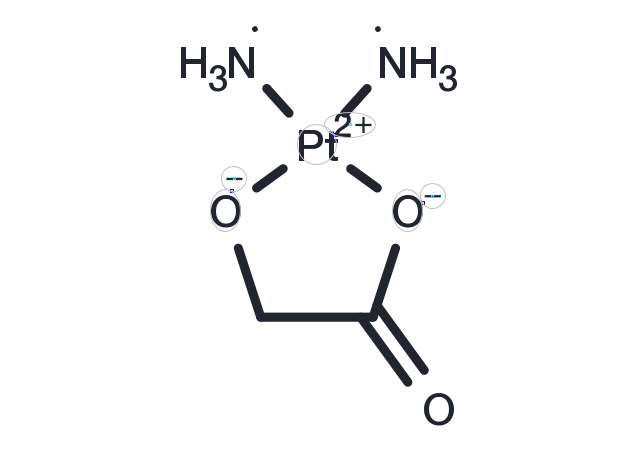
Nedaplatin (NSC-375101D) is a derivative of cisplatin and DNA damage agent for tumor colony forming units (IC50: 94 μM). Containing a novel ring structure in which glycolate is bound to the platinum by a bidentate ligand, nedaplatin forms reactive platinum complexes that bind to nucleophilic groups in DNA, resulting in intrastrand and interstrand DNA cross-links, apoptosis and cell death.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 35.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 68.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 126.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 187.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 463.00 |



| Description | Nedaplatin (NSC-375101D) is a derivative of cisplatin and DNA damage agent for tumor colony forming units (IC50: 94 μM). Containing a novel ring structure in which glycolate is bound to the platinum by a bidentate ligand, nedaplatin forms reactive platinum complexes that bind to nucleophilic groups in DNA, resulting in intrastrand and interstrand DNA cross-links, apoptosis and cell death. |
| Targets&IC50 | DNA damage:94 μM |
| In vitro | Compared to the use of each of the three drugs individually, pre-treating with 5-FU continuously before Nedaplatin or Cisplatin (FN or FC treatment) demonstrates a synergistic enhancement in inhibiting tumor growth and extending survival time. |
| In vivo | Nedaplatin (Aqupla), a derivative of cisplatin, inhibits tumor clonogenic colony formation with an IC50 of 28.5 μg/mL. At concentrations ranging from 0.005 to 0.5 μg/mL, Nedaplatin suppresses the proliferation of SBC-3 cells by 2% to 98%, with an IC50 of 0.053 μg/mL. |
| Cell Research | The inhibition of cell (including human SCLC cell line SBC-3 and human NSCLC cell line PC-14) proliferation after drug treatments as the antitumor activity using a regrowth assay is messured. Briefly, cells are exposed to drugs alone or in combination for 6 days at 37°C in an atmosphere of 100% humidity with 5% CO2; the cells are then pipetted six to eight times until almost all cells appeared as single cells and counted with a counter. For each drug, concentration-effect curves are drawn as plots of the fraction of surviving cells (unaffected cell fraction, fu) versus drug concentration. The cell proliferation ratio of the treated:control cultures (T:C%) is calculated as follows: [(the number of treated cells on day 6)/(the number of treated cells on day 0)]/[(the number of control cells on day 6)/(the number of control cells on day 0)] × 100%. The IC50 is defined as the drug concentration required for a 50% reduction in the number of cells. Four or five independent experiments are carried out for each. To check the effect of the drug treatment schedule on the effect of the combination, the cells are treated either by simultaneous exposure to the two drugs or by sequential exposure to Nedaplatin followed by irinotecan (Nedaplatin→irinotecan) and vice versa (irinotecan→Nedaplatin) for 3 hours. For the sequential exposure treatment, cells are exposed to the first drug for 3 hours, ished in fresh medium once, and then immediately exposed to the second drug for 3 hours. The treated cells are cultured in drug-free medium until evaluation.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC 375101D |
| Molecular Weight | 303.17 |
| Formula | C2H8N2O3Pt |
| CAS No. | 95734-82-0 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: Insoluble
H2O: 10 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Nedaplatin 95734-82-0 Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair DNA/RNA Synthesis Inhibitor NSC 375101D inhibit inhibitor
