Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


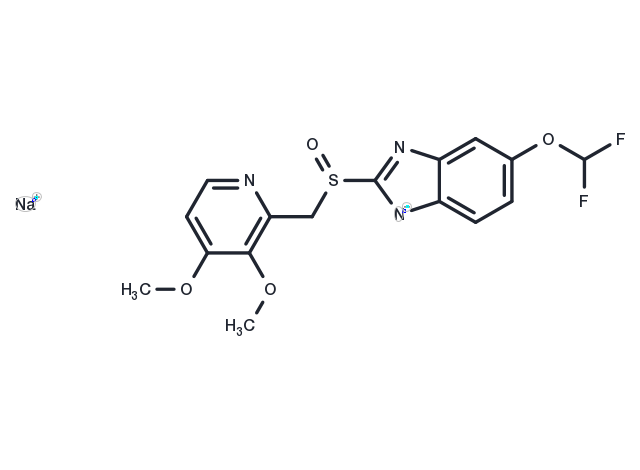
Pantoprazole sodium (Pantecta) is the sodium salt form of a substituted benzimidazole with proton pump inhibitor activity. Pantoprazole sodium is a lipophilic, weak base that crosses the parietal cell membrane and enters the acidic parietal cell canaliculus where it becomes protonated, producing the active metabolite sulfenamide, which forms an irreversible covalent bond with two sites of the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme located on the gastric parietal cell, thereby inhibiting both basal and stimulated gastric acid production.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 50.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 68.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |



| Description | Pantoprazole sodium (Pantecta) is the sodium salt form of a substituted benzimidazole with proton pump inhibitor activity. Pantoprazole sodium is a lipophilic, weak base that crosses the parietal cell membrane and enters the acidic parietal cell canaliculus where it becomes protonated, producing the active metabolite sulfenamide, which forms an irreversible covalent bond with two sites of the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme located on the gastric parietal cell, thereby inhibiting both basal and stimulated gastric acid production. |
| In vitro | pantoprazole (PPZ) inhibits tumor cells proliferation, inducs apoptosis and decreases the expression of HIF-1α protein[2]. Pantoprazole affects the intracellular distribution of HIF-1α in SGC-7901 cells, which might be one of the mechanisms of its chemosensitizing effect on cancer cells[3]. |
| In vivo | After PPZ treatment, apoptotic cell death is seen selectively in cancer cells and is accompanied with extracellular signal-regulated kinase deactivation. By contrast, normal gastric mucosal cells show the resistance to PPZ-induced apoptosis through the overexpression of antiapoptotic regulators including HSP70 and HSP27. In a xenograft model of nude mice, administration of PPZ significantly inhibits tumorigenesis and induces large-scale apoptosis of tumor cells[4]. |
| Cell Research | Pantoprazole sodium salts are resuspended in normal saline (0.85%) at 5 mg/ml immediately prior to use. When the SGC-7901 cells have reached 60–70% confluence, PPZ is added at a final concentration of 20 µg/ml, and the cells are cultured for additional experiments. For example, The SGC-7901 cells are seeded in 100 µl of medium per well, at a density of 1×104/well, in 96-well plates and treated with PPZ for 24 h. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Pantecta, SKF96022 sodium, SKF96022 (sodium), BY1023 (sodium), BY-1023 sodium, Pantoloc |
| Molecular Weight | 405.35 |
| Formula | C16H14F2N3NaO4S |
| CAS No. | 138786-67-1 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 75 mg/mL (185 mM)
H2O: 74 mg/mL (182.6 mM)
Ethanol: 75 mg/mL (185 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Pantoprazole sodium 138786-67-1 Angiogenesis Apoptosis Autophagy Chromatin/Epigenetic Membrane transporter/Ion channel Others Proton pump HIF stability Pantecta inhibit anti-secretory SKF-96022 BY-1023 SKF96022 sodium H+/K+-ATPase BY1023 SKF96022 (sodium) exosome BY1023 (sodium) PPI orally BY 1023 MCF-7 Pantoprazole Proton Pump Doxorubicin Inhibitor SKF 96022 anti-ulcer SKF96022 BY-1023 sodium release A431 Pantoloc inhibitor
