Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Phytic acid (Fytic Acid) is a complexing agent for removal of traces of heavy metal ions. It acts also as a hypocalcemic agent.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 40.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 55.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 87.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 126.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 183.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 453.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |


| Description | Phytic acid (Fytic Acid) is a complexing agent for removal of traces of heavy metal ions. It acts also as a hypocalcemic agent. |
| In vitro | Phytic acid, a major phosphorus storage compound of most seeds and cereal grains, contributes about 1 to 7% of their dry weight. It may account for more than 70% of the total kernel phosphorus. Phytic acid has the strong ability to chelate multivalent metal ions, especially zinc, calcium, and iron. The binding can result in very insoluble salts that are poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, which results in poor bioavailability of minerals. Phytic acid is also considered to be a natural antioxidant and is suggested to have potential functions of reducing lipid peroxidation and as a preservative in foods[1]. Phytic acid inhibits the formation of uric acid from xanthine with an IC50 of about 30 mM. The generation of the superoxide is greatly affected by phytic acid; the IC50 is about 6 mM, indicating that the superoxide generating domain of XO is more sensitive to phytic acid[2]. There has been observed an inhibition of tumor growth and induction of cell differentiation in the presence of phytic acid in a few cancer cell lines including colon, nipple, breast, prostate, cervix, liver, pancreas, melanoma and glioblastoma[3]. |
| In vivo | Phytic acid has a neuroprotective effect in MPTP-induced PD model and the neuroprotection is correlated with its anti-inflammatory effect which may be associated with suppression of pathways that involved in NF-κB and p-ERK. Phytic acid significantly inhibits MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell loss in the substantia nigra (SN). Moreover, using immunohistochemistry method and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), microglial activation and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) are found to be markedly repressed by phytic acid[4]. |
| Source |
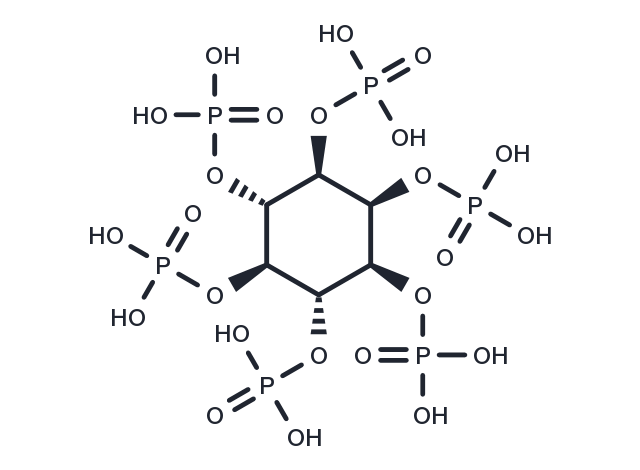
| Synonyms | Inositol hexaphosphate, inositol hexakisphosphate, inositol polyphosphate, myo-Inositol, hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate), Fytic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 660.04 |
| Formula | C6H18O24P6 |
| CAS No. | 83-86-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 55 mg/mL (83.33 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Phytic acid 83-86-3 Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite Xanthine Oxidase Inositol hexaphosphate inositol hexakisphosphate inositol polyphosphate Inositol Hexaphosphate myo-Inositol, hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate) Inhibitor Inositol inhibit Fytic Acid inhibitor
