Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Plantainoside D (Isoplantamajoside) shows potent antioxidative effects as those of ascorbic acid, it shows angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory inhibitory activity in vitro with the IC(50) value of 2.17 mM, it also shows inhibitory activity against PKCalpha with the IC50 value14.8microM.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 122.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 298.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 452.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 745.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 1,050.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 1,390.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 395.00 |



| Description | Plantainoside D (Isoplantamajoside) shows potent antioxidative effects as those of ascorbic acid, it shows angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory inhibitory activity in vitro with the IC(50) value of 2.17 mM, it also shows inhibitory activity against PKCalpha with the IC50 value14.8microM. |
| Targets&IC50 | ACE:2.17 mM , PKC:14.8microM |
| In vitro | Plantago asiatica L. and its major constituents(such as Plantainoside D) have ACE inhibitory activity in vitro. The identified compounds contribute to the angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity of the extract[1].In vitro, Adriamycin(ADR) caused dose-dependent toxicity in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells. Pre-treatment of the cardiac muscle cells with Plantainoside D(PD) significantly reduced ADR-induced apoptosis of cardiac muscle cells. PD inhibited the ROS produced by ADR in the cardiac muscle cells. As well, PD increased GSH(glutathione), compared with ADR. In response to ADR, NF-kappaB was activated in H9c2 cells. However the treatment of PD reduced the activation of NF-kappaB.The NF-kappaB inhibitor, PDTC, inhibited the cytotoxic effect on ADR-induced apoptosis in cardiac muscle cells. IkappaBalpha-dominant negative plasmid-overexpression abrogated ADR-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Ethanolic extract of the seeds of Plantago asiatica L. showed significant inhibitory activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) determined by monitoring the transformation from a substrate hippuryl-histidyl-leucine (HHL) to the product hippuric acid (HA) in vitro using an UPLC-MS method. The bioguided fractionation of the extract resulted in the isolation of four ACE inhibitory active phenylpropanoid glycosides acteoside, isoacteoside, Plantainoside D, and plantamajoside with IC(50) values of 2.69 mM, 2.46 mM, 2.17 mM, and 2.47 mM, respectively. Their structures were elucidated through the analysis of NMR, UV, IR and MS data[1]. |
| Source |
| Synonyms | Isoplantamajoside |
| Molecular Weight | 640.59 |
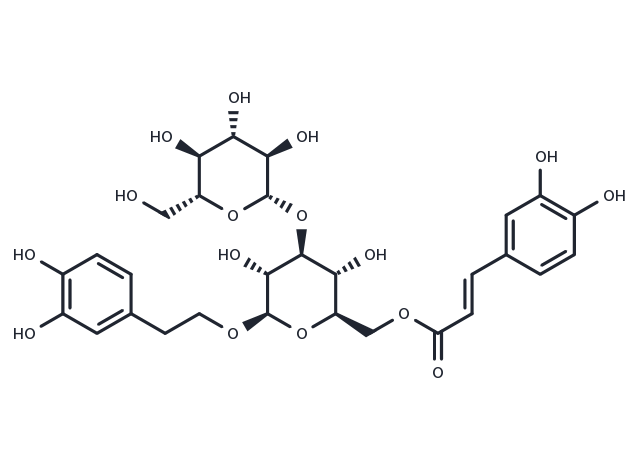
| Formula | C29H36O16 |
| CAS No. | 147331-98-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 10 mg/mL (15.6 mM), Sonification is recommended.
DMSO: 10 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Plantainoside D 147331-98-4 Chromatin/Epigenetic Cytoskeletal Signaling Endocrinology/Hormones RAAS PKC I kappa B kinase Inhibitor IKK Isoplantamajoside Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibit IκB kinase inhibitor
