Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Prostaglandin E1 (Alprostadil) is the naturally occurring prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) which displays a variety of pharmacologic actions. Prostaglandin E1 is a potent vasodilator agent that increases peripheral blood flow, inhibits platelet aggregation, and induces bronchodilation. Used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, this agent produces corporal smooth muscle relaxation by binding to PGE receptors, resulting in the activation of adenylate cyclase and the subsequent accumulation of 3'5'-cAMP.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 30.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 39.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 63.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 96.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 196.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 382.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 553.00 | |
| 200 mg | In stock | $ 748.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 72.00 |



| Description | Prostaglandin E1 (Alprostadil) is the naturally occurring prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) which displays a variety of pharmacologic actions. Prostaglandin E1 is a potent vasodilator agent that increases peripheral blood flow, inhibits platelet aggregation, and induces bronchodilation. Used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, this agent produces corporal smooth muscle relaxation by binding to PGE receptors, resulting in the activation of adenylate cyclase and the subsequent accumulation of 3'5'-cAMP. |
| Synonyms | PGE1, Alprostadil |
| Molecular Weight | 354.48 |
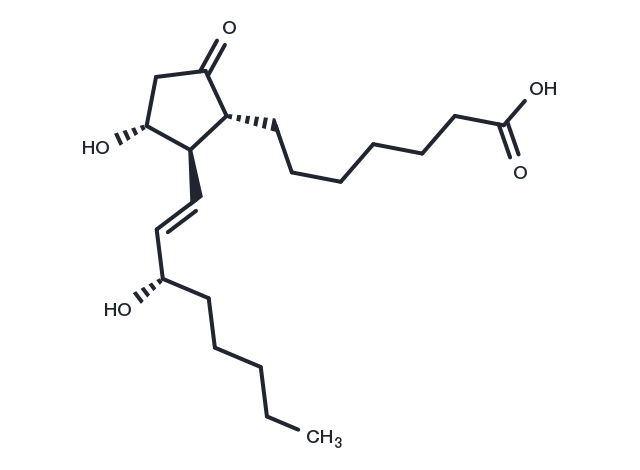
| Formula | C20H34O5 |
| CAS No. | 745-65-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Ethanol: 17.7 mg/mL (50 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Prostaglandin E1 745-65-3 GPCR/G Protein Immunology/Inflammation Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite Prostaglandin Receptor EP4 vasodilation EP3 PGE-1 PGE1 prostanoid Prostaglandin E-1 inhibit EP1 Prostaglandin E 1 aggregation PGE 1 Alprostadil Inhibitor vasodilator EP2 platelet inhibitor
