Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Semaxinib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR2 inhibitor (IC50: 1.23 μM), 20-fold more selective for VEGFR than PDGFRβ, lack of activity against InsR, EGFR, and FGFR. Semaxanib reversibly inhibits ATP binding to the tyrosine kinase domain of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), which may inhibit VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell migration and proliferation and reduce the tumor microvasculature.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 44.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 61.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 121.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 170.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 237.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |


| Description | Semaxinib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR2 inhibitor (IC50: 1.23 μM), 20-fold more selective for VEGFR than PDGFRβ, lack of activity against InsR, EGFR, and FGFR. Semaxanib reversibly inhibits ATP binding to the tyrosine kinase domain of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), which may inhibit VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell migration and proliferation and reduce the tumor microvasculature. |
| Targets&IC50 | VEGFR2:1.23 μM |
| In vitro | SU5416 inhibits VEGF-driven mitogenesis in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.04±0.02 μM (n=3). In contrast, SU5416 blocked FGF-dependent mitogenesis of HUVECs with an IC50 of 50 μM (n=10). The selective activity of SU5416 on Flk-1 is supported by the fact that testing of SU5416 using NIH 3T3 cells overexpressing either the EGF or insulin receptors indicated a complete lack of activity (IC50>100 μM). This observation is confirmed by immunoblotting after ligand stimulation. An IC50 of 20.26±5.2 μM (n=7), which is about 20-fold less in potency on PDGF-dependent autophosphorylation, is observed when SU5416 is tested in NIH 3T3 cells overexpressing the human PDGF receptor β[1]. |
| In vivo | Administering SU5416 daily (i.p., 3 mg/kg/day) effectively inhibits C6 tumor growth in the colon, achieving a growth inhibition of 62% by day 16 (P=0.001), comparable to the 54% inhibition in the hindflank by day 18 (P=0.001). This demonstrates SU5416's potential to suppress tumor development in various locations, possibly due to differences in preexisting vasculature. Further, a higher dose of SU5416 (25 mg/kg) significantly reduces tumor growth rates, with tumors being only 8% the size of those in control animals by day 22, primarily through a substantial decrease in the area covered by newly formed glioma microvasculature in treated animals, suggesting a minimized initial tumor vascularization. |
| Kinase Assay | Solubilized membranes from 3T3 Flk-1 cells are added to polystyrene ELISA plates that has been precoated with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes Flk-1. After an overnight incubation with lysate at 4°C, serial dilutions of SU5416 are added to the immunolocalized receptor. To induce autophosphorylation of the receptor, various concentrations of ATP are added to the ELISA plate wells containing serially diluted solutions of SU5416. The autophosphorylation is allowed to proceed for 60 min at room temperature and then stopped with EDTA. The amount of phosphotyrosine present on the Flk-1 receptors in the individual wells is determined by incubating the immunolocalized receptor with a biotinylated monoclonal antibody directed against phosphotyrosine. After removal of the unbound anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, avidin-conjugated horseradish peroxidase H is added to the wells. A stabilized form of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethyl benzidine dihydrochloride and Water2 is added to the wells. The color readout of the assay is allowed to develop for 30 min, and the reaction is stopped with H2SO4. Parallel biochemical kinase assays are performed to measure autophosphorylation on EGFR and fibroblast growth factor receptor[1]. |
| Cell Research | SU5416 is dissolved in DMSO and stored,and then diluted with appropriate media (DMSO<0.5%) before use[1] 3T3Her2 and 488 g2M2 are NIH3T3 fibroblast cell lines engineered to overexpress Her2 and to express human PDGF-BB and human PDGF receptor β.Both cell lines are cultured in DMEM supplemented with 2% CS and 2 mM L-glutamine.C6,Calu 6,A375,A431,and SF767T are plated in their respective growth medium at 2×103 cells/100 μL/well in 96-well,flat-bottomed plates.SU5416 is serially diluted in media containing DMSO (<0.5%) and added to cultures of tumor cells 1 day after the initiation of culture.Cell growth is measured after 96 h using the sulforhodamine B method.IC50s are calculated by curve fitting using four-parameter analysis[1]. |
| Synonyms | SU5416 |
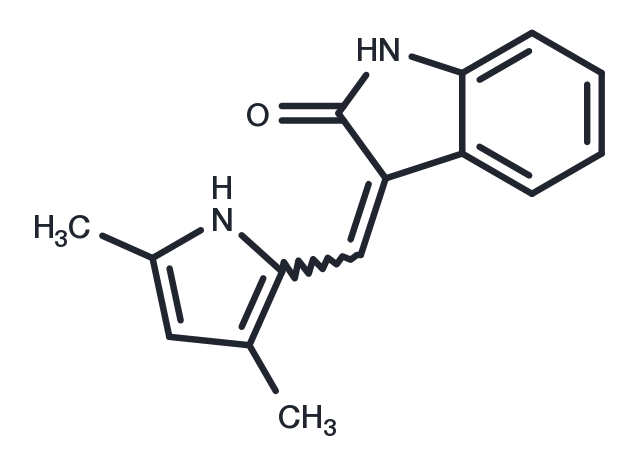
| Molecular Weight | 238.28 |
| Formula | C15H14N2O |
| CAS No. | 204005-46-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 2.38 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonification is recommended
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Semaxinib 204005-46-9 Angiogenesis Tyrosine Kinase/Adaptors VEGFR SU-5416 Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibit Inhibitor SU5416 SU 5416 inhibitor
