Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Cysteamine hydrochloride (Thioethanolamine Hydrochloride) is an agent for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis and an antioxidant.
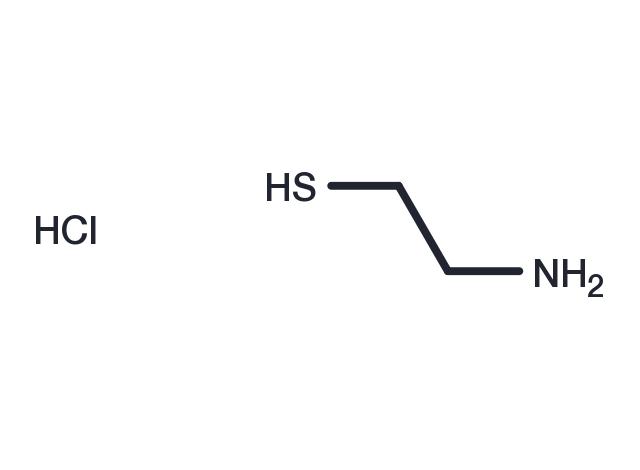
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 42.00 | |
| 5 g | In stock | $ 50.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 46.00 |


| Description | Cysteamine hydrochloride (Thioethanolamine Hydrochloride) is an agent for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis and an antioxidant. |
| In vitro | Cysteamine enhances intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels in cystinotic cells, effectively restoring their altered redox state and demonstrating antioxidant capabilities by increasing glutathione production, thus scavenging harmful OH and HOCl. It also mitigates increased apoptosis rates in cystinotic cells by counteracting the effects of elevated caspase 3 and protein kinase Cε activity. Furthermore, Cysteamine boosts the production of various heat shock proteins (HSP), notably murine Hsp40. It exhibits a dose-dependent mitigation of doxorubicin-induced death in cancer cells, including HeLa and B16 cells, without affecting cell survival on its own. Remarkably, it enhances the efficacy of doxorubicin in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells, significantly increasing cell death. Additionally, Cysteamine (100 μM) not only heightens intracellular GSH levels but also improves the development of matured oocytes to the blastocyst stage in embryo cultures. [1][2] |
| In vivo | Cysteamine is introduced as a treatment for cystinosis by depleting lysosomal cystine. Cystamine can inhibit transglutaminase activity by binding to the cysteine in its active center. Cysteamine increases brain levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is caused by the increased expression of the heat shock DNAJ-containing protein 1 (HSJ1). Cysteamine inhibits the formation of gastric and mammary tumors that are induced chemically or after irradiation, respectively. The administration of Cysteamine is also able to inhibit the metastasis of pancreatic cancer in a mouse model by decreasing the expression and activity of metalloproteinases. [1] |
| Synonyms | 2-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride, β-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride, Thioethanolamine Hydrochloride, 2-Aminoethanethiol Hydrochloride, Cysteamine HCl, Bekaptan |
| Molecular Weight | 113.61 |
| Formula | C2H7NS·HCl |
| CAS No. | 156-57-0 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Ethanol: 22 mg/mL (193.6 mM)
H2O: 21 mg/mL (184.8 mM)
DMSO: 22 mg/mL (193.6 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Cysteamine hydrochloride 156-57-0 Apoptosis Autophagy Immunology/Inflammation Metabolism NF-Κb Others Reactive Oxygen Species Endogenous Metabolite cystinosis b-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride antioxidant 2-Aminoethanethiol nephropathic 2-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride Inhibitor Cysteamine β-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride Thioethanolamine Hydrochloride 2-Aminoethanethiol Hydrochloride inhibit Cysteamine Hydrochloride beta-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride orally 2-Mercaptoethylamine Cysteamine HCl Bekaptan inhibitor
