High Standards for Entry Criteria
In high-throughput screening (HTS), the quality of the compound library directly determines the accuracy and reliability of the screening results. TargetMol’s Natural Product Library has established extremely high entry standards to ensure that every compound in the library is a structurally defined and high-purity monomer compound. We not only exclude compounds with ambiguous structures, such as mixtures and polymers llike Casanthranol and Heparan Sulfate, but also ensure structural accuracy and high purity of each monomer compound through stringent quality control processes.
Remarkable Structural Diversity
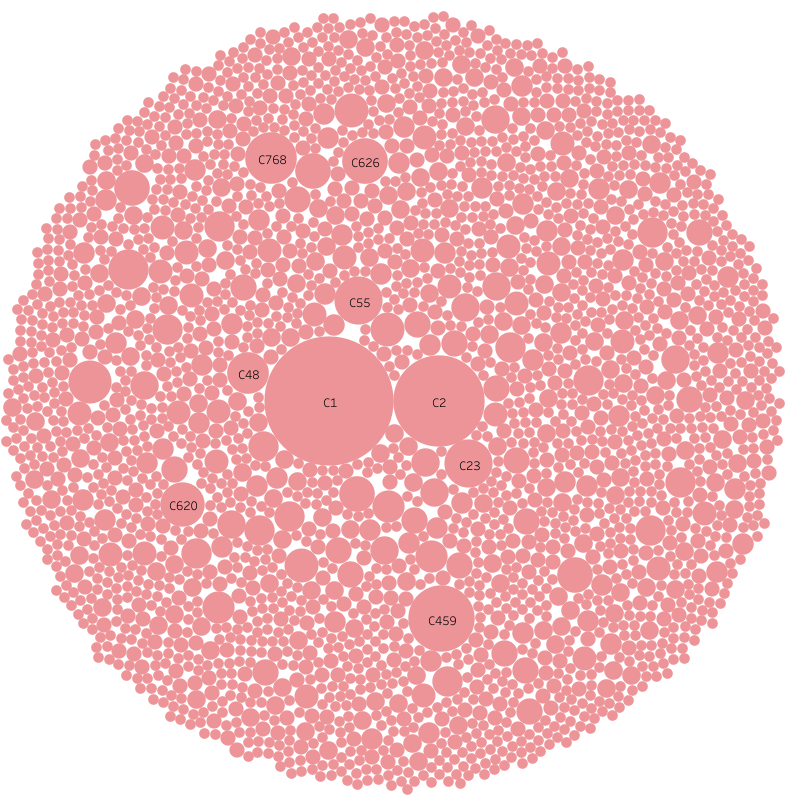
TargetMol’s Natural Product Library features rich scaffold diversity and structural complexity, including multiple chiral centers and higher molecular rigidity, showcasing significant advantages in new drug discovery. TargetMol’s Natural Product Library can be classified into 2,624 categories based on MACCS molecular fingerprints. Its abundant chemical structural diversity provides a solid foundation for identifying novel lead compounds, greatly promoting pharmaceutical innovation.
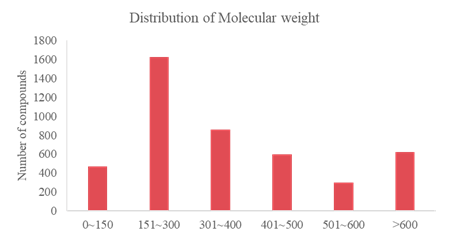
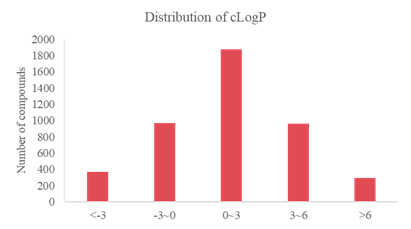
Library Diversity Analysis
Superior Potential for Proprietary Drugs
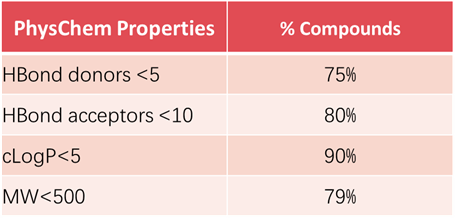
65% of natural products in TargetMol’s Natural Product Library comply with Lipinski's "Rule of Five" (Ro5), as exemplified by RO5 Drug-like Natural Product Library (L6160), indicating that TargetMol's natural products possess excellent bioavailability and permeability.
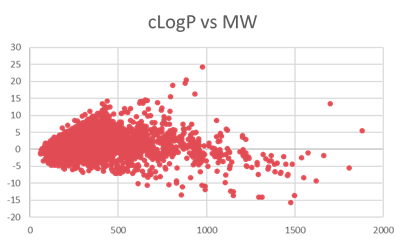
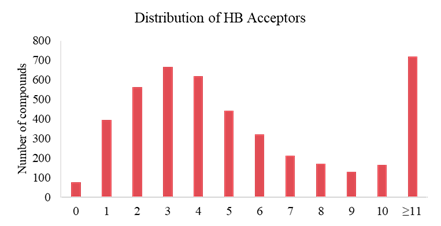
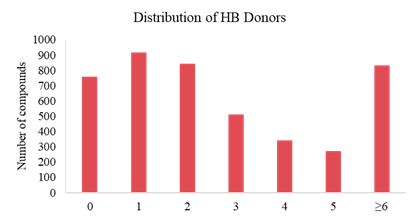
Analysis on Drug-like Parameter
Multidimensional Pharmacokinetic Analysis
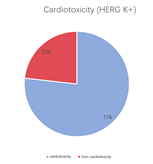
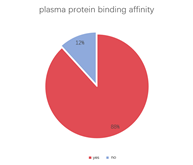
A multi-dimensional evaluation was conducted on TargetMol’s Natural Product Library, covering key pharmacological parameters such as blood-brain barrier penetration, cardiotoxicity (hERG K+ channel blocking), plasma protein binding rate, intestinal absorption, oral and dermal absorption performance, among others.
• 13% of compounds can cross the blood-brain barrier, while 87% cannot.
• 77% of compounds exhibit cardiotoxicity, while 23% do not.
• 88% of compounds show a plasma protein binding within a reasonable range, while 12% fall outside the reasonable range.
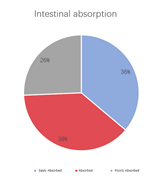
• 36% of compounds are highly absorbable in the small intestine, 38% are absorbable in the small intestine, and 26% are poorly absorbable in the small intestine.
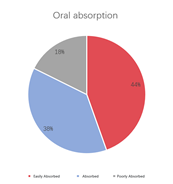
• 44% of compounds are highly orally absorbable, 38% are orally absorbable, and 18% are poorly orally absorbable.
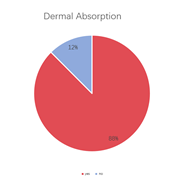
• 88% of compounds are absorbable through the skin, while 12% are poorly absorbable through the skin.
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty