- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
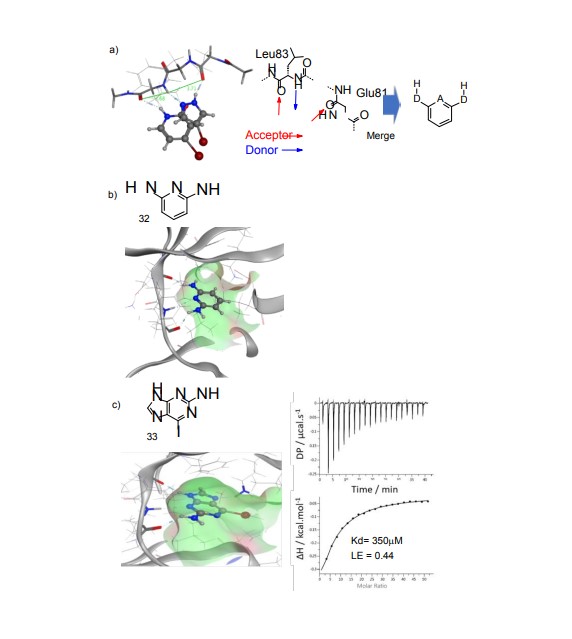
The theoretical basis of FBDD is to select favorable fragment combinations or extensions to obtain new drug molecules, with a higher probability of obtaining highly active drug candidates. Compared with the screening of millions of macromolecules, thousands of fragment molecules can be combined to form millions of drug structures, which are easier to collect and manage. In addition, fragments have smaller molecular weights, relatively higher solubility, and easier structural optimization. The potential of over-the-counter medicine is higher. The FragLites identify productive drug-like interactions, which are identified sensitively and unambiguously by X-ray crystallography, exploiting the anomalous scattering of the halogen substituent. This mapping of protein interaction surfaces provides an assessment of druggability and can identify efficient start points for the de novo design of hit molecules incorporating the interacting motifs. Combine fragments from FragLites to generate fragment lead compounds: