Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CLPS Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in Baculovirus insect cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 11.5 kDa and the accession number is P04118.

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 μg | $386 | In Stock | |
| 200 μg | $660 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $1,340 | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | Activity testing is in progress. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| Description | CLPS Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in Baculovirus insect cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 11.5 kDa and the accession number is P04118. |
| Species | Human |
| Expression System | Baculovirus Insect Cells |
| Tag | C-His |
| Accession Number | P04118 |
| Synonyms | colipase, pancreatic |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CLPS (P04118) (Met 1-Gln 112) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. Predicted N terminal: Ala 18 |
| Protein Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 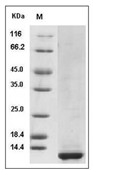 |
| Molecular Weight | 11.5 kDa (predicted); 12 kDa (reducing conditions) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, 500 mM NaCl, pH 7.0, 10% gly. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Colipase belongs to the colipase family. Structural studies of the complex and of colipase alone have revealed the functionality of its architecture. It is a small protein with five conserved disulphide bonds. Structural analogies have been recognised between a developmental protein, the pancreatic lipase C-terminal domain, the N-terminal domains of lipoxygenases and the C-terminal domain of alpha-toxin. Colipase can only be detected in pancreatic acinar cells, suggesting regulation of expression by tissue-specific elements. Colipase allows lipase to anchor noncovalently to the surface of lipid micelles, counteracting the destabilizing influence of intestinal bile salts. Without colipase the enzyme is washed off by bile salts, which have an inhibitory effect on the lipase. Colipase is a cofactor needed by pancreatic lipase for efficient dietary lipid hydrolysis. It binds to the C-terminal, non-catalytic domain of lipase, thereby stabilising as active conformation and considerably increasing the overall hydrophobic binding site. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.