- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
IRAK4 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4, also known as Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-64, IRAK-4, and IRAK4, is a member of the protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and Pelle subfamily. IRAK4 contains one death domain and one protein kinase domain. IRAK4 is required for the efficient recruitment of IRAK1 to the IL-1 receptor complex following IL-1 engagement, triggering intracellular signaling cascades leading to transcriptional up-regulation and mRNA stabilization. It also phosphorylates IRAK1. A member of the IL-1 receptor (IL-1R)-associated kinase (IRAK) family, IRAK4, has been shown to play an essential role in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated signaling. IL-1-mediated IRAK4 kinase activity in T cells is essential for the induction of IL-23R expression, Th17 differentiation, and autoimmune disease. Pharmacological blocking of IRAK4 kinase activity will retain some levels of host defense while reducing the levels and duration of inflammatory responses, which should provide beneficial therapies for sepsis and chronic inflammatory diseases. Defects in IRAK4 are the cause of recurrent isolated invasive pneumococcal disease type 1 (IPD1) which is defined as two episodes of IPD occurring at least 1 month apart, whether caused by the same or different serotypes or strains. Recurrent IPD occurs in at least 2% of patients in most series, making IPD the most important known risk factor for subsequent IPD. Defects in IRAK4 are also the cause of IRAK4 deficiency which causes extracellular pyogenic bacterial and fungal infections in otherwise healthy children.

IRAK4 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μg | $320 | In Stock | |
| 100 μg | $567 | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μg | $1,000 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $2,120 | 7-10 days |
Product Information
| Biological Activity | The specific activity was determined to be 169 nmol/min/mg using MBP as substrate. |
| Description | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4, also known as Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-64, IRAK-4, and IRAK4, is a member of the protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and Pelle subfamily. IRAK4 contains one death domain and one protein kinase domain. IRAK4 is required for the efficient recruitment of IRAK1 to the IL-1 receptor complex following IL-1 engagement, triggering intracellular signaling cascades leading to transcriptional up-regulation and mRNA stabilization. It also phosphorylates IRAK1. A member of the IL-1 receptor (IL-1R)-associated kinase (IRAK) family, IRAK4, has been shown to play an essential role in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated signaling. IL-1-mediated IRAK4 kinase activity in T cells is essential for the induction of IL-23R expression, Th17 differentiation, and autoimmune disease. Pharmacological blocking of IRAK4 kinase activity will retain some levels of host defense while reducing the levels and duration of inflammatory responses, which should provide beneficial therapies for sepsis and chronic inflammatory diseases. Defects in IRAK4 are the cause of recurrent isolated invasive pneumococcal disease type 1 (IPD1) which is defined as two episodes of IPD occurring at least 1 month apart, whether caused by the same or different serotypes or strains. Recurrent IPD occurs in at least 2% of patients in most series, making IPD the most important known risk factor for subsequent IPD. Defects in IRAK4 are also the cause of IRAK4 deficiency which causes extracellular pyogenic bacterial and fungal infections in otherwise healthy children. |
| Species | Human |
| Expression System | Baculovirus Insect Cells |
| Tag | N-His |
| Accession Number | Q9NWZ3-1 |
| Synonyms | REN64,NY-REN-64,IRAK-4,IPD1,interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human IRAK4 (Q9NWZ3-1) (Met 1-Ser 460) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. Predicted N terminal: Met |
| Protein Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 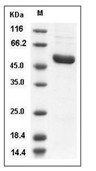 |
| Molecular Weight | 53.8 kDa (predicted); 48 kDa (reducing conditions) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM PMSF, pH 7.4. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store the product under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. Samples are stable for up to 12 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4, also known as Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-64, IRAK-4, and IRAK4, is a member of the protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and Pelle subfamily. IRAK4 contains one death domain and one protein kinase domain. IRAK4 is required for the efficient recruitment of IRAK1 to the IL-1 receptor complex following IL-1 engagement, triggering intracellular signaling cascades leading to transcriptional up-regulation and mRNA stabilization. It also phosphorylates IRAK1. A member of the IL-1 receptor (IL-1R)-associated kinase (IRAK) family, IRAK4, has been shown to play an essential role in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated signaling. IL-1-mediated IRAK4 kinase activity in T cells is essential for the induction of IL-23R expression, Th17 differentiation, and autoimmune disease. Pharmacological blocking of IRAK4 kinase activity will retain some levels of host defense while reducing the levels and duration of inflammatory responses, which should provide beneficial therapies for sepsis and chronic inflammatory diseases. Defects in IRAK4 are the cause of recurrent isolated invasive pneumococcal disease type 1 (IPD1) which is defined as two episodes of IPD occurring at least 1 month apart, whether caused by the same or different serotypes or strains. Recurrent IPD occurs in at least 2% of patients in most series, making IPD the most important known risk factor for subsequent IPD. Defects in IRAK4 are also the cause of IRAK4 deficiency which causes extracellular pyogenic bacterial and fungal infections in otherwise healthy children. |
Dose Conversion
Calculator
Tech Support

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.


