- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Fetal-tau Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
MAPT (microtubule-associated protein tau) can produce tau proteins. Tau proteins are proteins that stabilize microtubules. They are abundant in neurons of the central nervous system and are less common elsewhere, but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. When tau proteins are defective, and no longer stabilize microtubules properly, they can result in dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Tau protein is a highly soluble microtubule-associated protein (MAP). In humans, these proteins are mostly found in neurons compared to non-neuronal cells. One of tau's main functions is to modulate the stability of axonal microtubules. Other nervous system MAPs may perform similar functions, as suggested by tau knockout mice, who did not show abnormalities in brain development - possibly because of compensation in tau deficiency by other MAPs.

Fetal-tau Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μg | $386 | In Stock | |
| 100 μg | $660 | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μg | $1,120 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $2,270 | 7-10 days |
Product Information
| Biological Activity | Activity testing is in progress. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| Description | MAPT (microtubule-associated protein tau) can produce tau proteins. Tau proteins are proteins that stabilize microtubules. They are abundant in neurons of the central nervous system and are less common elsewhere, but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. When tau proteins are defective, and no longer stabilize microtubules properly, they can result in dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Tau protein is a highly soluble microtubule-associated protein (MAP). In humans, these proteins are mostly found in neurons compared to non-neuronal cells. One of tau's main functions is to modulate the stability of axonal microtubules. Other nervous system MAPs may perform similar functions, as suggested by tau knockout mice, who did not show abnormalities in brain development - possibly because of compensation in tau deficiency by other MAPs. |
| Species | Human |
| Expression System | E. coli |
| Tag | N-His |
| Accession Number | P10636-2 |
| Synonyms | TAU,PPP1R103,PPND,MTBT2,MTBT1,MSTD,microtubule-associated protein tau,MAPTL,MAPT,FTDP-17,DDPAC |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human MAPT (NP_058525.1) (Ala2-Leu352) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. Predicted N terminal: His |
| Protein Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 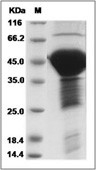 |
| Molecular Weight | 38.7 kDa (predicted); 40-50 kDa (reducing conditions) |
| Endotoxin | Please contact us for more information. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, pH 7.4. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | MAPT (microtubule-associated protein tau) can produce tau proteins. Tau proteins are proteins that stabilize microtubules. They are abundant in neurons of the central nervous system and are less common elsewhere, but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. When tau proteins are defective, and no longer stabilize microtubules properly, they can result in dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Tau protein is a highly soluble microtubule-associated protein (MAP). In humans, these proteins are mostly found in neurons compared to non-neuronal cells. One of tau's main functions is to modulate the stability of axonal microtubules. Other nervous system MAPs may perform similar functions, as suggested by tau knockout mice, who did not show abnormalities in brain development - possibly because of compensation in tau deficiency by other MAPs. |
Dose Conversion
Calculator
Tech Support

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.


