Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

PT4 is a treatment agent for Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL). PT4 decreases of mitochondrial membrane potential and increases reactive oxygen species production, therefore leads to parasite death. PT4 is effective against both species of Leishmania. The IC50 values of PT4 against L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis are 125.18 and 233.18 μM , respectively. PT4 also shows potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo [1].
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,520 | 6-8 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $1,980 | 6-8 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $2,500 | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | PT4 is a treatment agent for Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL). PT4 decreases of mitochondrial membrane potential and increases reactive oxygen species production, therefore leads to parasite death. PT4 is effective against both species of Leishmania. The IC50 values of PT4 against L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis are 125.18 and 233.18 μM , respectively. PT4 also shows potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo [1]. |
| In vitro | PT4 (0-1256.5 μM, 48 hours) effectively inhibits the viability of mammalian cells and demonstrates significant antiparasitic activity against L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis promastigotes and amastigotes, with dosages ranging from 314.1-19.6 μM over 48 hours. It induces mitochondrial membrane depolarization in these parasites, leading to an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the mitochondria. In cytotoxicity assays, PT4 showed varying inhibitory effects on Balb/c mice peritoneal exudate cells (mPEC), J774A.1 macrophages, and fibroblasts, with half-maximal cytotoxic concentration (CC50) values of 981.37 μM, 521.47 μM, and 895.17 μM, respectively. Additionally, cell proliferation assays revealed that PT4 inhibited the proliferation of L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis promastigotes with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 70.46 μM and 181.73 μM, respectively, and their amastigote forms with IC50 values of 125.18 μM and 233.18 μM, respectively. |
| In vivo | The pharmacokinetic and toxicological analysis of PT4 demonstrates its chemical characteristics and effects within specified parameters. It adheres to the Hydrogen Bond Acceptor (HBA) criterion of 4 (≤10), lacks Hydrogen Bond Donors (HBD) with a count of 0 (≤5), and possesses a LogP value of 2.23 (≤5), indicating moderate lipophilicity. The molecular weight (MW) is well within the acceptable range at 318.33 g/mol (≤500). PT4 exhibits an optimal number of rotatable bonds (n-ROTB) at 4 (≤10) and a Topological Polar Surface Area (TPSA) of 68.09 Ų, aligning with effective permeability characteristics. It is acknowledged for its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB Yes), demonstrates a high gastrointestinal absorption (GIA High), and is not a P-Glycoprotein (P-GP) substrate. Skin permeability is indicated by a log value of -6.85 cm/s. Its interaction with Cytochrome P450 enzymes shows it as an inhibitor of 2C9, 2C19, and 1A2, while not inhibiting 2D6 and 3A4, highlighting selective metabolic interactions. The total clearance rate is noted at a log value of 0.117 ml/min/kg, with no significant reaction as a renal Organic Cation Transporter 2 (OCT2) substrate. The lethal dose 50 (LD50) is recorded at 4700 mg/kg, suggesting a relatively safe profile within certain exposure limits. |
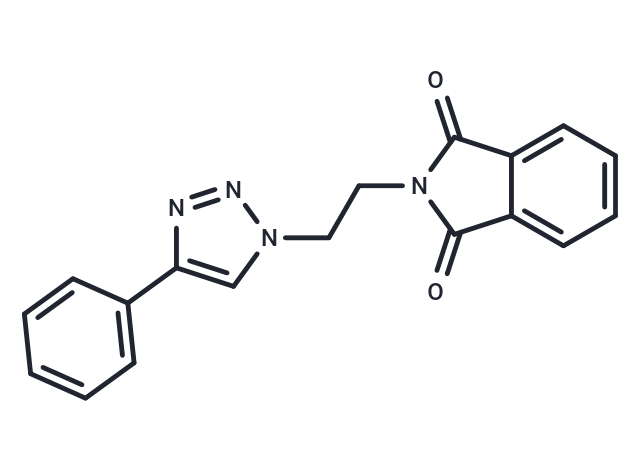
| Molecular Weight | 318.33 |
| Formula | C18H14N4O2 |
| Cas No. | 1280738-47-7 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.