Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

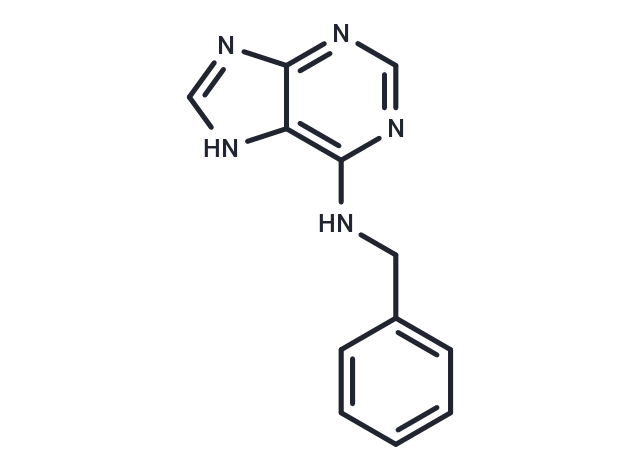
6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BAP), benzyl adenine or BAP is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $112 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $52 | In Stock |
| Description | 6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BAP), benzyl adenine or BAP is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. |
| In vitro | 6-BA promotes plant branching, increases resistance to disease, drought, cold, or high salt levels and increases flowering and fruit set by decreasing flower drop[1]. |
| Alias | N6-Benzyladenine, Benzyladenine, BA, 6-BAP |
| Molecular Weight | 225.25 |
| Formula | C12H11N5 |
| Cas No. | 1214-39-7 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 34.62 mg/mL (153.68 mM) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.