- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
FGF-9 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
Fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF-9) is an approximately 26 kDa secreted glycoprotein of the FGF family. Secreted mouse FGF-9 lacks the N-terminal 1-3 aa and shares >98% sequence identity with rat, human, equine, porcine and bovine FGF-9. FGF-9 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. In the mouse embryo the location and timing of FGF-9 expression affects development of the skeleton, cerebellum, lungs, heart, vasculature, digestive tract, and testes .It may have a role in glial cell growth and differentiation during development, gliosis during repair and regeneration of brain tissue after damage, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of glial tumors. Deletion of mouse FGF-9 is lethal at birth due to lung hypoplasia, and causes rhizomelia, or shortening of the proximal skeleton. An unusual constitutive dimerization of FGF 9 buries receptor interaction sites which lowers its activity, and increases heparin affinity which inhibits diffusion. A spontaneous mouse mutant, Eks, interferes with dimerization, resulting monomeric, diffusible FGF-9 that causes elbow and knee synostoses (joint fusions) due to FGF-9 misexpression in developing joints.

FGF-9 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 μg | $82 | In Stock | |
| 20 μg | $133 | 7-10 days | |
| 50 μg | $249 | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μg | $382 | 7-10 days |
Product Information
| Biological Activity | Activity has not been tested. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| Description | Fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF-9) is an approximately 26 kDa secreted glycoprotein of the FGF family. Secreted mouse FGF-9 lacks the N-terminal 1-3 aa and shares >98% sequence identity with rat, human, equine, porcine and bovine FGF-9. FGF-9 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. In the mouse embryo the location and timing of FGF-9 expression affects development of the skeleton, cerebellum, lungs, heart, vasculature, digestive tract, and testes .It may have a role in glial cell growth and differentiation during development, gliosis during repair and regeneration of brain tissue after damage, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of glial tumors. Deletion of mouse FGF-9 is lethal at birth due to lung hypoplasia, and causes rhizomelia, or shortening of the proximal skeleton. An unusual constitutive dimerization of FGF 9 buries receptor interaction sites which lowers its activity, and increases heparin affinity which inhibits diffusion. A spontaneous mouse mutant, Eks, interferes with dimerization, resulting monomeric, diffusible FGF-9 that causes elbow and knee synostoses (joint fusions) due to FGF-9 misexpression in developing joints. |
| Species | Mouse |
| Expression System | E. coli |
| Tag | N-6xHis |
| Accession Number | P54130 |
| Synonyms | heparin-binding growth factor-9,HBGF-9,Glia-activating factor,GAF,Fibroblast growth factor 9,Fgf-9,Fgf9 |
| Amino Acid | Met1Ser208 |
| Construction | Met1Ser208 |
| Protein Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. (QC verified) 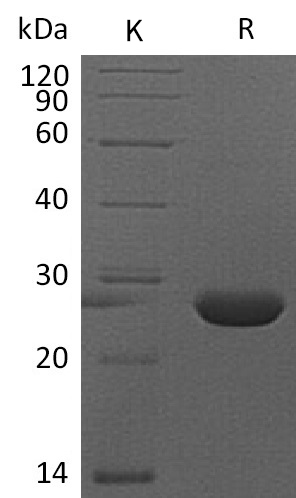 |
| Molecular Weight | 25 KDa (reducing condition) |
| Endotoxin | < 0.001 ng/µg (0.01 EU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5% Trehalose, 1 mM EDTA, 20% Glycerol, 1 mM DTT, pH 8.5. |
| Stability & Storage | Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF-9) is an approximately 26 kDa secreted glycoprotein of the FGF family. Secreted mouse FGF-9 lacks the N-terminal 1-3 aa and shares >98% sequence identity with rat, human, equine, porcine and bovine FGF-9. FGF-9 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. In the mouse embryo the location and timing of FGF-9 expression affects development of the skeleton, cerebellum, lungs, heart, vasculature, digestive tract, and testes .It may have a role in glial cell growth and differentiation during development, gliosis during repair and regeneration of brain tissue after damage, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of glial tumors. Deletion of mouse FGF-9 is lethal at birth due to lung hypoplasia, and causes rhizomelia, or shortening of the proximal skeleton. An unusual constitutive dimerization of FGF 9 buries receptor interaction sites which lowers its activity, and increases heparin affinity which inhibits diffusion. A spontaneous mouse mutant, Eks, interferes with dimerization, resulting monomeric, diffusible FGF-9 that causes elbow and knee synostoses (joint fusions) due to FGF-9 misexpression in developing joints. |
Dose Conversion
Calculator
Tech Support

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.


