Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Dihydromunduletone (DHM) is an adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (aGPCR) antagonist that acts as a chemical probe for the inhibition of GPR56 and GPR114/ADGRG5, which have similar tethered agonists.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $179 | 7-10 days |
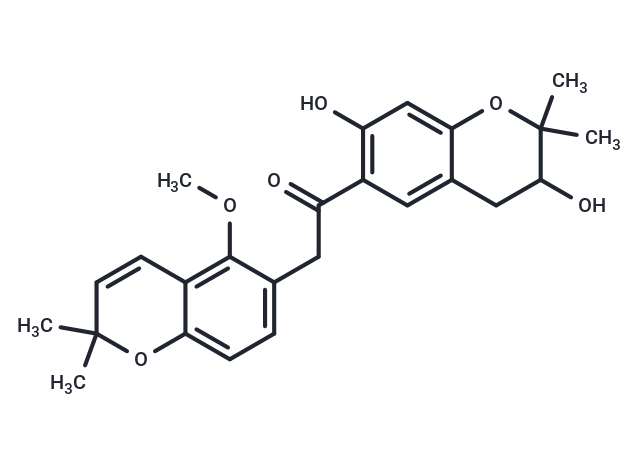
| Description | Dihydromunduletone (DHM) is an adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (aGPCR) antagonist that acts as a chemical probe for the inhibition of GPR56 and GPR114/ADGRG5, which have similar tethered agonists. |
| Targets&IC50 | GPR56:20.9 μM |
| In vitro | Assays commence with the addition of [35S]GTPγS, and the rates of aGPCR-stimulated G protein activation (Gα binding to [35S]GTPγS) are assessed with or without added compounds. Dihydromunduletone (DHM) significantly inhibits the kinetics of GPR56 7TM-stimulated G13 GTPγS binding, reducing activation by over 75%. At 50 μM DHM maximally inhibits GPR56 and dramatically reduces GPR114 7TM-stimulated Gs activity, but fails to inhibit GPR110 7TM stimulation of Gq GTPγS binding. Cells transfected with GPR56 A386M 7TM show concentration-dependent inhibition of P7 peptide-induced luciferase activity by DHM. Additionally, 3 μM DHM blunts P7 peptide activation at all concentrations. In conclusion, DHM antagonizes synthetic-peptide and tethered-peptide agonist-mediated aGPCR activation in isolated membranes and HEK293T cell-based assays but does not inhibit basal receptor signaling. |
| Alias | DHM |
| Molecular Weight | 424.49 |
| Formula | C25H28O6 |
| Cas No. | 674786-20-0 |
| Smiles | O(C)C1=C2C(=CC=C1CC(=O)C=3C=C4C(=CC3O)OC(C)(C)C(O)C4)OC(C)(C)C=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.223 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 20 mg/mL (47.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.