Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

JC-1 (CBIC2) is a fluorescent lipophilic carbocyanine dye. It has been used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. JC 1 can be used in a probe for measuring mitochondrial membrane potential by flow cytometry.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $59 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $81 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $153 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $252 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $423 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $628 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $893 | In Stock |
| Description | JC-1 (CBIC2) is a fluorescent lipophilic carbocyanine dye. It has been used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. JC 1 can be used in a probe for measuring mitochondrial membrane potential by flow cytometry. |
| In vitro | JC-1 fluorescence is usually excited by the 488nm laser wavelength common in flow cytometers[1]. JC-1 (2.5μM) exposed to murine L1210 lymphoblasts, can be detected the presence of both cytoplasmic JC-1 monomer and mitochondrial J-aggregates in these cells. Fluorescent labeling of mitochondria with either JC-1 (1 μg/mL, 15 min), reveals that are distributed irregularly, resulting in regions of high and low mitochondrial content within astrocytes[2]. JC-1 is avidly accumulated in sensitive K562 cells where it displays both a green cytoplasmic and red mitochondrial fluorescence. JC-1 is poorly accumulated in resistant K562 cells, which displays only a slight green fluorescence[4]. JC-1 has been shown to interact with α-synuclein at the acidic C-terminal region with a Kd of 2.6 μM. JC-1 itself does not accelerate the protein aggregation of α-synuclein in the absence of iron, insted, it decelerates the aggregation process by extending the lag phase approx[3]. |
| Alias | CBIC2 |
| Molecular Weight | 652.23 |
| Formula | C25H27Cl4IN4 |
| Cas No. | 3520-43-2 |
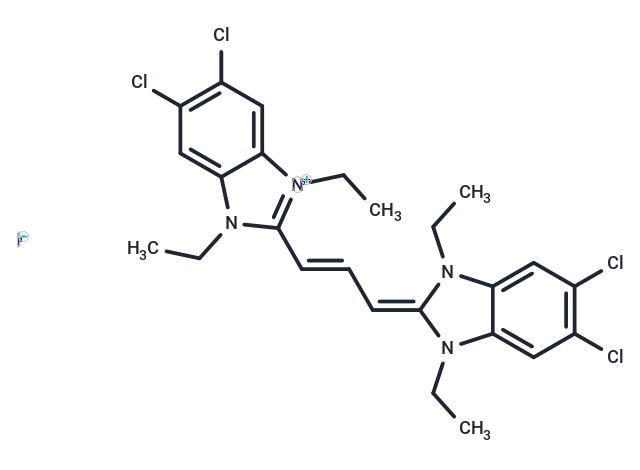
| Smiles | [I-].CCN1C(=C\C=C\c2n(CC)c3cc(Cl)c(Cl)cc3[n+]2CC)N(CC)c2cc(Cl)c(Cl)cc12 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 14 mg/mL (21.46 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.