Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

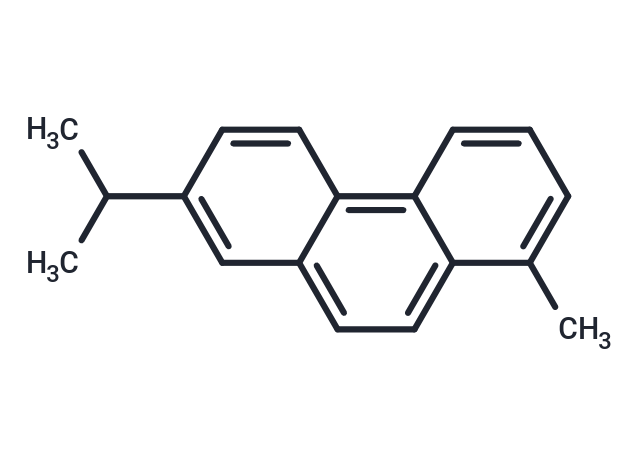
Retene (NSC-26317) is widely present in recent and ancient sediments, and compounds can be extracted from fir forest soils, humic coals, terrestrial petroleum hydrocarbon source rocks, and deep-sea sediments.Retene is produced by dehydrogenation of pine acids during petrogenesis.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $163 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $410 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $597 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $973 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $1,290 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,770 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $3,550 | In Stock |
| Description | Retene (NSC-26317) is widely present in recent and ancient sediments, and compounds can be extracted from fir forest soils, humic coals, terrestrial petroleum hydrocarbon source rocks, and deep-sea sediments.Retene is produced by dehydrogenation of pine acids during petrogenesis. |
| Targets&IC50 | Whitefish larvae:13.3 microg/L(LC50) |
| In vitro | In laboratory conditions whitefish larvae were pre-exposed to retene (10, 32 and 100 microg/l), with relevant controls, and irradiated in semi-static tests for 3 h once a day (2 consecutive days) with two UV-B doses (CIE-weighted 2.8 or 5.4 kJ per m(2) per day) or with visible light only. The photoinduced acute LC(50) for retene was 13.3 microg/L. Retene treated fish exhibited signs of behavioral irritation and hypoxia during and after the exposure to UV light. Severe skin damages were detected in larvae exposed simultaneously to retene and UV-B. The structural signs of sunburn could also be seen in UV-B and solvent controls (DMSO) with UV-B. Even at the lowest retene concentration, the number of mucous cells increased significantly in simultaneous chemical and UV-B treatment. We consider the tissue reaction as protective response against UV induced retene toxicity. Further, regarding liver parenchyma, fish exposed to retene with UV-B had lesions, revealing hepatotoxicity.[1] |
| In vivo | Retene (7-isopropyl-1-methylphenanthrene) is a naturally formed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) that causes teratogenicity in fish larvae and induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP1A) enzymes. Retene occurs at high concentrations (< or =3,300 microg/g dry wt) in surface sediments contaminated by resin acids from pulp mill effluents. Industrially contaminated sediments collected near a bleached kraft pulp and paper mill discharging to Lake Saimaa, Finland, significantly induced trout liver CYP1A activity, indicating accumulation of arylhydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-active ligands. Induction of CYP1A in fish exposed to sediments spiked with retene or benzo[k]fluoranthene supported this conclusion.[2] |
| Alias | NSC-26317, NSC26317, NSC 26317 |
| Molecular Weight | 234.34 |
| Formula | C18H18 |
| Cas No. | 483-65-8 |
| Smiles | CC=1C=2C(=C3C(C=C(C(C)C)C=C3)=CC2)C=CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.0350 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 18.33 mg/mL (78.22 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.