Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

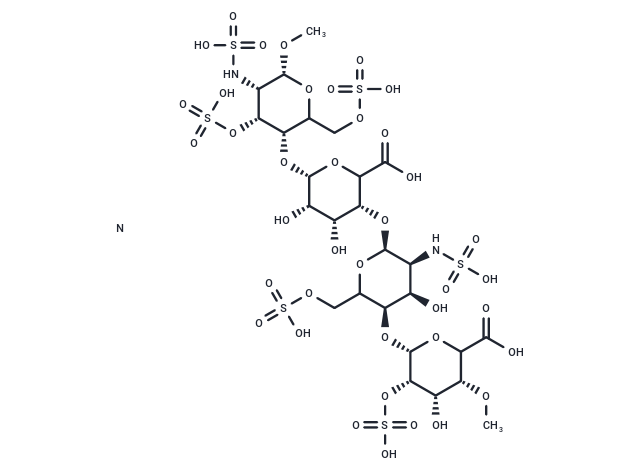
Heparan sulfate is a natural product, a linear polysaccharide. Heparan sulfate occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG) that is tightly attached to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $44 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $163 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $322 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $538 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $777 | In Stock |
| Description | Heparan sulfate is a natural product, a linear polysaccharide. Heparan sulfate occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG) that is tightly attached to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Breast cancer cells MDA-MB231 were treated with Heparan sulfate (20 µg/mL) for 24 h and detected by Fluorescence microscopy. RESULTS: Cell spreading was enhanced and the average spreading cell area approximately doubled in the presence of Heparan sulfate. Exogenous Heparan sulfate blocked cell invasion and matrix degradation. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay anti-tumor activity in vivo, Heparan sulfate (0.8 mg/kg) was administered to SCID-hu mice injected with bone marrow aspirates from myeloma patients twice daily, once intraperitoneally and once subcutaneously, for four weeks. RESULTS: Treatment with Heparan sulfate significantly inhibited primary tumor growth in a human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID-hu) myeloma model. [2] |
| Molecular Weight | 593.47(monomer) |
| Formula | C12H19NO20S3 (monomer) |
| Cas No. | 9050-30-0 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Insoluble H2O: 100 mg/mL (168.50 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.