Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

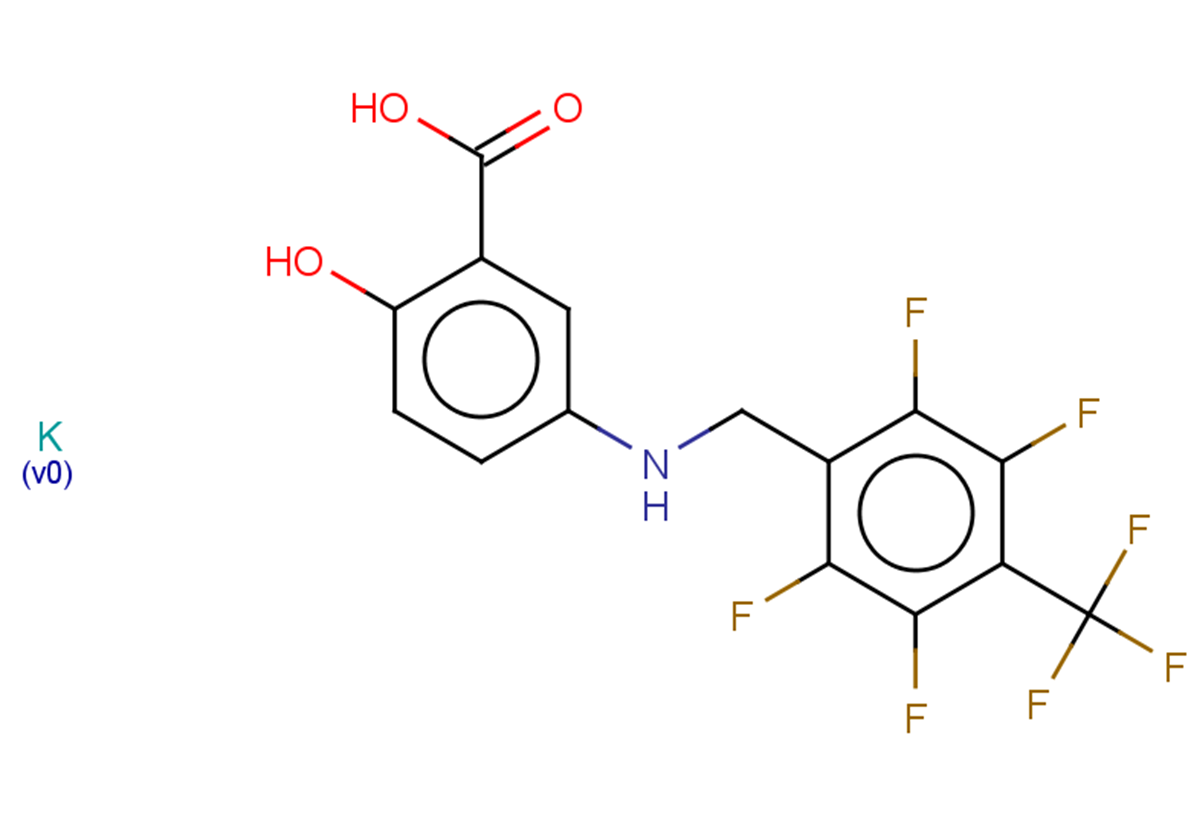
Nelonemdaz potassium (also known as Salfaprodil) is a potent NR2B-selective and uncompetitive antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA). This compound exhibits remarkable neuroprotection against cell death induced by both NMDA and free radicals, in addition to its role as a free radical scavenger.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $239 | 1-2 weeks |
| Description | Nelonemdaz potassium (also known as Salfaprodil) is a potent NR2B-selective and uncompetitive antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA). This compound exhibits remarkable neuroprotection against cell death induced by both NMDA and free radicals, in addition to its role as a free radical scavenger. |
| In vitro | Nelonemdaz potassium demonstrates neuroprotective effects by effectively counteracting 300 μM N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) toxicity with doses starting as low as 30 μM and inhibiting cultured cortical neurons' electrophysiologic responses to 300 μM NMDA in a concentration-dependent manner. Even at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 1 μM, it significantly mitigates Fe2+-induced neurotoxicity and prevents the degeneration of neurons and glia in cortical cell cultures. Moreover, Nelonemdaz potassium exhibits potent antioxidant properties by scavenging superoxide, nitric oxide, and hydroxyl radicals with respective IC50 values of 63.07±1.44 μM, 155.8±4.88 μM, and 58.45±1.74 μM. It also decreases antimycin A-induced ROS/RNS production and malondialdehyde (MDA) formation in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 2.21±0.11 μM and 2.72±0.26 μM, respectively, and effectively reduces iron-ascorbate-induced lipid peroxidation (IC50 = 24.56±0.07 μM). |
| In vivo | Nelonemdaz potassium, administered intravenously at dosages ranging from 0.5-20 mg/kg, significantly reduces the size of cerebral infarcts 24 hours post a 60-minute middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in a dose-dependent manner. At a specific dosage of 5 mg/kg, it notably protects both white matter, including axons and myelin, and gray matter from ischemic brain damage. Studies conducted on male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 260 to 300 g using two different occlusion models—clip and intraluminal thread occlusion—revealed that a dosage of 0.5-20 mg/kg administered 5 minutes after reperfusion could lead to a significant neuroprotective effect, peaking with a 66% reduction in infarct volume at dosages between 2.5 and 5 mg/kg. Specifically, at a 5 mg/kg dosage, it prevented neuronal damage in critically vulnerable cortical areas. Further, under the intraluminal thread occlusion model, the same 5 mg/kg dosage given 30 minutes post-reperfusion did not alter physiological parameters (arterial pH, PCO2, PO2, hematocrit) but effectively reduced infarct volumes in the cortex and striatum and markedly diminished white matter damage in the striatum and external capsule. |
| Alias | Salfaprodil, Neu2000potassium |
| Molecular Weight | 421.31 |
| Formula | C15H7F7KNO3 |
| Cas No. | 916214-57-8 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.