Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Actinonin ((-)-Actinonin) is a naturally occurring antibacterial agent produced by Actinomyces and a potent reversible peptide deformylase (PDF) inhibitor with a Ki of 0.28 nM. It also induces apoptosis and inhibits aminopeptidase M, aminopeptidase N, and leucine aminopeptidase, as well as MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-8, MMP-9, and meprin α with Ki values of 300 nM, 1,700 nM, 190 nM, 330 nM, and 20 nM, respectively. Actinonin exhibits antiproliferative and antitumor activities [1][2][3][4][5].
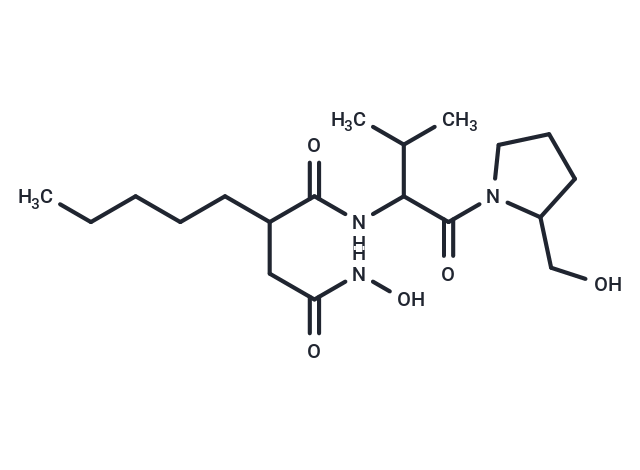

| Description | Actinonin ((-)-Actinonin) is a naturally occurring antibacterial agent produced by Actinomyces and a potent reversible peptide deformylase (PDF) inhibitor with a Ki of 0.28 nM. It also induces apoptosis and inhibits aminopeptidase M, aminopeptidase N, and leucine aminopeptidase, as well as MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-8, MMP-9, and meprin α with Ki values of 300 nM, 1,700 nM, 190 nM, 330 nM, and 20 nM, respectively. Actinonin exhibits antiproliferative and antitumor activities [1][2][3][4][5]. |
| Targets&IC50 | PDF:(ki)0.28 nM |
| In vitro | Actinonin is a chemical compound that effectively inhibits the growth of various human tumor cells, displaying IC50 values ranging from 4 μM to 49.3 μM across multiple cell lines, including Raji, MDA-MB-468, PC3, SK-LC-19, Hela, HT-1080, and AL67[1]. It induces tumor-specific effects, such as mitochondrial membrane depolarization and ATP depletion, in a time- and dose-dependent manner[1]. Furthermore, Actinonin exhibits antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive bacteria, like S. aureus (MIC 8-16 μg/mL), Streptococcus pyogenes (MIC 8 μg/mL), and Streptococcus epidermidis (MIC 2-4 μg/mL), and Gram-negative bacteria, including H. influenzae (MIC 1-2 μg/mL), Moraxella catarrhalis (MIC 0.5 μg/mL), and Neisseria gonorrheae (MIC 1-4 μg/mL), with notable effectiveness against efflux pump mutants of H. influenzae and E. coli (MIC values of 0.13 μg/mL and 0.25 μg/mL, respectively)[2]. Actinonin targets HsPDF within mitochondria, leading to cell death in tumors, and is a potent inhibitor of peptide deformylases (PDF) from both S. aureus and E. coli, with IC50 values as low as 0.8 nM for Fe-PDF (E. coli) under assay conditions[2]. |
| In vivo | Actinonin, administered safely to mice at doses up to 400 mg/kg as an antibiotic, exhibits remarkable antitumor activity in both intraperitoneal (i.p.) and oral forms in a CWR22 human prostate tumor xenograft model in nude mice, with no observed toxicity[1]. Furthermore, despite its in vitro antitumor efficacy, Actinonin demonstrates no significant toxicity to normal tissues. |
| Alias | (-)-Actinonin |
| Molecular Weight | 385.5 |
| Formula | C19H35N3O5 |
| Cas No. | 13434-13-4 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.