Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

TD52 dihydrochloride (TD52 2HCl), a derivative of Erlotinib, is a potent and orally active inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A). It exhibits strong anti-cancer properties by regulating the CIP2A/PP2A/p-Akt signaling pathway, resulting in the induction of apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Mechanistically, TD52 dihydrochloride disrupts the binding of Elk1 to the CIP2A promoter, effectively reducing CIP2A levels. Notably, TD52 dihydrochloride demonstrates powerful anti-cancer activity while displaying less inhibition of p-EGFR.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $76 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $172 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $271 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $397 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | TD52 dihydrochloride (TD52 2HCl), a derivative of Erlotinib, is a potent and orally active inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A). It exhibits strong anti-cancer properties by regulating the CIP2A/PP2A/p-Akt signaling pathway, resulting in the induction of apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Mechanistically, TD52 dihydrochloride disrupts the binding of Elk1 to the CIP2A promoter, effectively reducing CIP2A levels. Notably, TD52 dihydrochloride demonstrates powerful anti-cancer activity while displaying less inhibition of p-EGFR. |
| In vitro | TD52 dihydrochloride, at concentrations ranging from 2 to 10 μM over 48 hours, exhibits an anti-proliferative capacity and triggers differential apoptotic reactions in various cell lines. Specifically, at a concentration of 5 μM for 48 hours, it shows negligible impacts on both p-EGFR and EGFR levels, while notably reducing CIP2A expression. Moreover, across dosages of 2.5, 5, and 7.5 μM for 48 hours, TD52 dihydrochloride progressively induces apoptosis, which is associated with the suppression of CIP2A and p-Akt. Additionally, at a concentration of 5 μM over 24 hours, it considerably enhances the phosphatase activity of PP2A in TNBC cells. At the same 5 μM concentration but extended to 48 hours, TD52 dihydrochloride does not significantly affect other common receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), such as IGFR, PDGFR, and VEGFR2[1]. |
| In vivo | TD52 dihydrochloride, administered orally at a dosage of 10 mg/kg/day through gavage for a duration of 52 days, significantly reduces the size and weight of MDA-MB-468 xenograft tumors[1]. |
| Alias | TD52 dihydrochloride(1798328-24-1 Free base), TD52 2HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 433.33 |
| Formula | C24H18Cl2N4 |
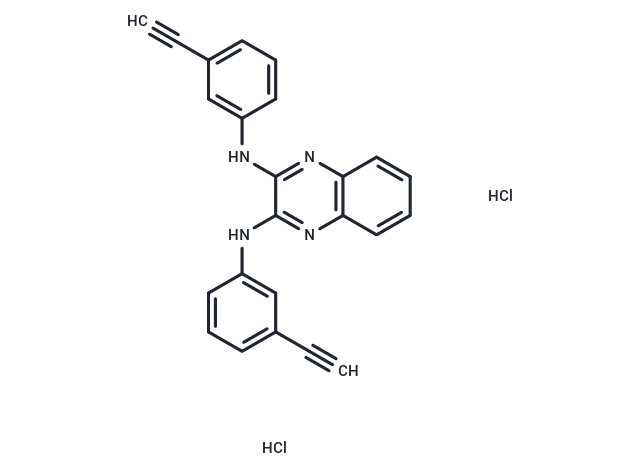
| Smiles | C#CC1=CC=CC(NC2=NC3=C(N=C2NC4=CC(C#C)=CC=C4)C=CC=C3)=C1.Cl.Cl |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 22.5 mg/mL (51.9 mM), Sonication and heating to 60℃ are recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.