Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $42 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $75 | In Stock |
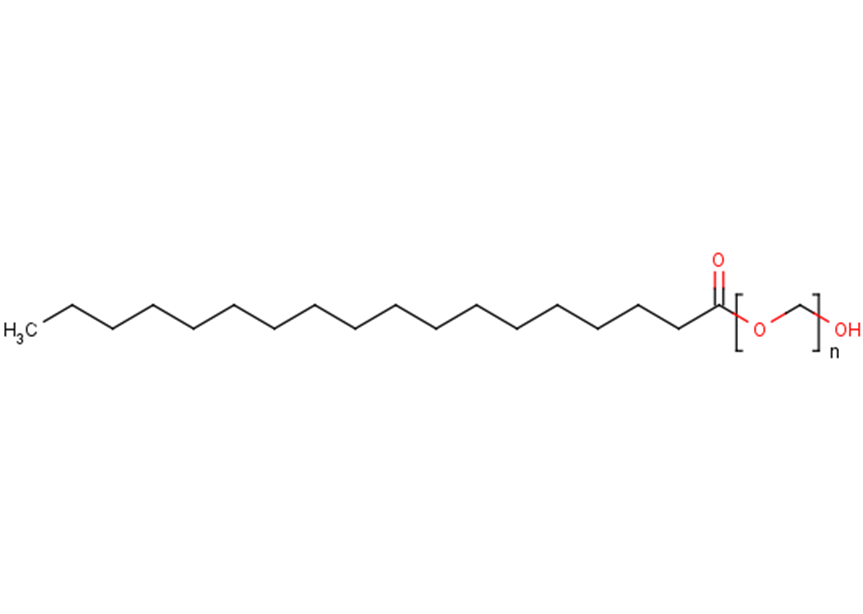
| Description | Polyoxyethylene stearate (POES) is an agent of non-ionic emulsifying. |
| In vitro | Polyoxyethylene stearate modulates P-gp ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner, reducing P-gp mediated efflux, notably enhancing the efficacy of substances like vinblastine sulfate by limiting their expulsion from cells. This compound is also recommended to augment the radiolabelled 7H12 Middlebrook TB media, significantly promoting mycobacterial growth in the BACTEC rapid culture system. Its effectiveness extends across various mycobacterial species beyond M. tuberculosis. Specifically, at concentrations of 100 or 150 μg/mL, polyoxyethylene 40 stearate substantially increases the cytotoxicity of vinblastine to K562/ADR cells. Moreover, polyoxyethylene (50) stearate markedly boosts mycobacterial growth rates and decreases detection times in cultures, illustrating its broad potential in enhancing antimicrobial and chemotherapeutic treatments. |
| In vivo | In the combination of polyoxyethylene 40 stearate and vinblastine, there is a significant reduction in both the average tumor volume and weight compared to the vinblastine group alone. The tumor growth inhibition rate markedly increases from 0.06 (vinblastine group) to 0.84 (vinblastine+polyoxyethylene 40 stearate group). Furthermore, polyoxyethylene stearate shows potential as a pharmaceutical excipient to enhance the oral bioavailability of drugs that are substrates for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and certain cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms [2][3]. |
| Alias | POES |
| Formula | C20H40O3 |
| Cas No. | 9004-99-3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (136.97 mM) |

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.