Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

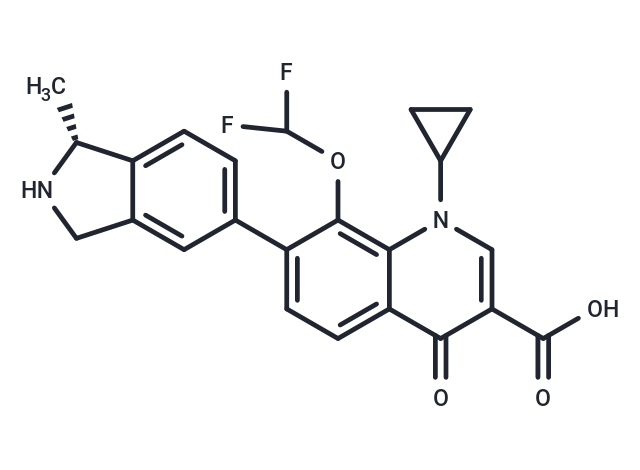
Garenoxacin (BMS284756) is a novel oral des-fluoro(6) quinolone for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | TBD | 35 days | |
| 10 mg | TBD | 35 days | |
| 25 mg | TBD | 35 days |
| Description | Garenoxacin (BMS284756) is a novel oral des-fluoro(6) quinolone for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections. |
| In vivo | The mean maximum plasma concentration (Cmax ) was 3.00 ± 1.12 μg/mL, time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax ) was 3.0 ± 2.0 hours, and area under the curve for 24 hours (AUC0-24 ) was 40.7 ± 16.7 μg·h/mL. The half-life (T1/2 ) of GRNX could not be calculated because plasma concentrations remained high 24 hours after administration. Cmax was strongly associated with the GRNX dose per kilogram body weight (r = 0.85, P = 0.03).Clinically, fever resolved within 3 days of GRNX administration and C-reactive protein levels returned to normal 14 days after administration. One patient experienced temporary increases in serum transaminase levels[1]. |
| Animal Research | Six male patients with infections who were undergoing MH received 200 mg GRNX once daily. Blood samples were taken before and at 1, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 hours after GRNX administration. Plasma GRNX concentrations were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography[1]. |
| Alias | BMS284756 |
| Molecular Weight | 426.41 |
| Formula | C23H20F2N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 194804-75-6 |
| Relative Density. | 1.421g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 2 mg/mL (4.69 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.