Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Guaifenesin (Guaiphenesin) is an expectorant that also has some muscle relaxing action. It is used in many cough preparations.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $35 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Guaifenesin (Guaiphenesin) is an expectorant that also has some muscle relaxing action. It is used in many cough preparations. |
| In vivo | Guaifenesin (200 mg/kg, intravenously) combined with ketamine (50 mg/kg, intramuscularly) produces effective and safe surgical anesthesia for over 30 minutes in New Zealand white rabbits. Guaifenesin (200 mg/kg, intravenously) combined with ketamine (50 mg/kg, intramuscularly) mildly depresses respiratory rate but heart rate and arterial blood pressure are not significantly affected. Guaifenesin (200 mg/kg, intravenously) is combined with sodium pentobarbital (20 mg/kg, intravenously) to produce surgical anesthesia for a period of more than 30 minutes. [1] Guaifenesin (50 mg/mL) combined Xylazine (0.1 mg/mL) and Ketamine (1.0 mg/mL) results in excellent anesthetic induction and maintenance with cardiopulmonary alterations similar to those associated with isoflurane in mechanically ventilated calves. [2] Guaifenesin (150 mg/kg) decreases spectral edge frequency (SEF) and total power in pigs. [3] Guaifenesin prevents adverse anesthetic induction events caused by Propofol in horse. Guaifenesin (90 mg/kg) followed by Propofol (3 mg/kg) should be sufficient to immobilize > 99% of calm healthy adult horses. [4] Guaifenesin (100 mg/kg) produces moderate behavioral changes in the social conflict test in mice. Guaifenesin (200 mg/kg) combined with Paracetamol (200 mg/kg) causes significantly more pronounced analgesic effects that the corresponding doses of paracetamol alone in mice. [5] |
| Alias | Guaiphenesin, Guaiacol glyceryl ether, Glycerol guaiacolate |
| Molecular Weight | 198.22 |
| Formula | C10H14O4 |
| Cas No. | 93-14-1 |
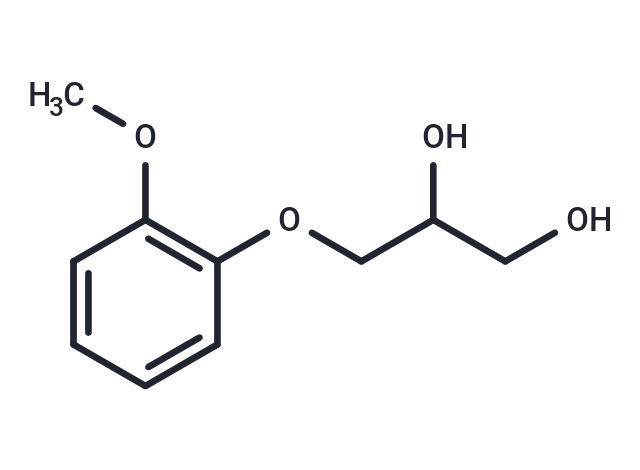
| Smiles | COC1=C(OCC(O)CO)C=CC=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.195 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (252.24 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 23 mg/mL (116.03 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 38 mg/mL (191.71 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.