Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

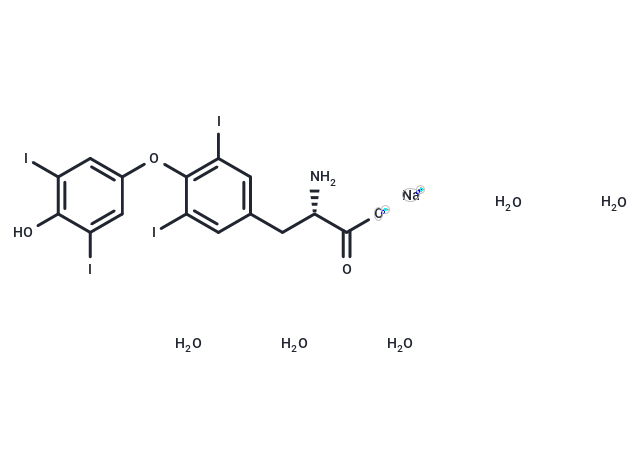
L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate (Sodium levothyroxine pentahydrate) is a thyroid hormone with anticholesterol activity that inhibits the release of thyroid hormones from thyroid cancer nodules and is used in immune and endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism, myxedema, cretinism and obesity. diseases, such as hypothyroidism, myxedema, cretinism and obesity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $30 | Backorder | |
| 500 mg | $50 | Backorder | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | Backorder |
| Description | L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate (Sodium levothyroxine pentahydrate) is a thyroid hormone with anticholesterol activity that inhibits the release of thyroid hormones from thyroid cancer nodules and is used in immune and endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism, myxedema, cretinism and obesity. diseases, such as hypothyroidism, myxedema, cretinism and obesity. |
| In vivo | In experimental rats fed a 12-week iodine-free diet, levels of triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine were significantly decreased compared to controls on a standard diet. In the low-dose L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate-treated group, an increase in L-thyroxine levels was observed, while triiodothyronine levels were virtually indistinguishable from those of the control group. Rats receiving high-dose L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate treatment had significantly increased circulating concentrations of triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine compared to the untreated hypothyroid group, and L-thyroxine levels were significantly increased compared to the control group. [2] |
| Alias | Sodium levothyroxine pentahydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 888.93 |
| Formula | C15H20I4NNaO9 |
| Cas No. | 6106-07-6 |
| Relative Density. | 2.381 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO: 20 mg/mL (22.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.