Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

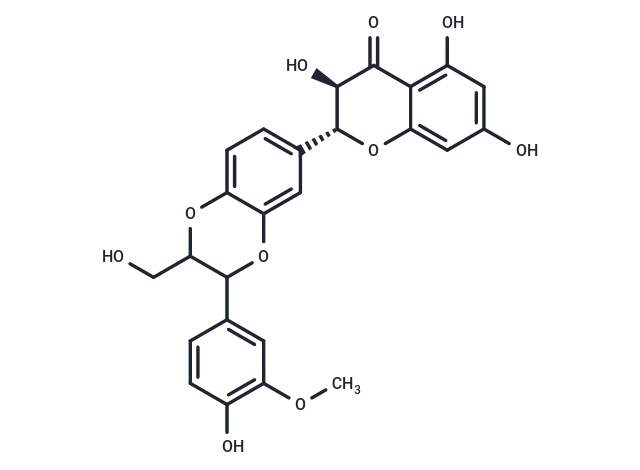
Silybin is a flavonoid from Silybum that inhibits P-glycoprotein-assisted extracellular efflux, inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes, has the advantage of being well-tolerated, can be used as an adjunctive treatment for hepatotoxicity and chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in cosmetic applications, as well as being capable of blocking the MCT8 transporter protein.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $62 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $90 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $129 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $325 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock |
| Description | Silybin is a flavonoid from Silybum that inhibits P-glycoprotein-assisted extracellular efflux, inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes, has the advantage of being well-tolerated, can be used as an adjunctive treatment for hepatotoxicity and chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in cosmetic applications, as well as being capable of blocking the MCT8 transporter protein. |
| In vitro | Methods: HepG2 cells were treated with Silybin (0-200 mM, 24, 48, 72 hours) and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Results: After 72 hours of treatment, the IC50 value was 68 μM. [1] |
| In vivo | Methods: C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet for 8 weeks and treated with Silybin (50 or 100 mg/kg per day) and sodium taurodeoxycholate (TUDCA, 50 mg/kg/day) by gavage in the last 4 weeks. Blood biochemical indices and liver lipid determination as well as liver Oil Red O staining were performed to evaluate the model and lipid-lowering effects of Silybin and TUDCA. In addition, serum and liver samples were detected by a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS)-based metabolomics platform. Multivariate/univariate data analysis and pathway analysis were used to study differential metabolites and metabolic pathways. Results: The mouse NAFLD model was successfully established, and Silybin and TUDCA significantly reduced serum and liver lipid accumulation. Metabolomics analysis of serum and liver showed that a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet led to abnormal metabolism of metabolites in lipid metabolism, polyol metabolism, amino acid metabolism, urea cycle, and TCA cycle. Both Silybin and TUDCA treatment reversed the metabolic disturbances induced by HFD feeding.[2] |
| Alias | Silibinin |
| Molecular Weight | 482.44 |
| Formula | C25H22O10 |
| Cas No. | 802918-57-6 |
| Smiles | C(O)C1C(OC=2C(O1)=CC=C(C2)[C@H]3OC=4C(C(=O)[C@@H]3O)=C(O)C=C(O)C4)C5=CC(OC)=C(O)C=C5 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | store at 4°C | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 20 mg/mL (41.46 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.