Shopping Cart
- Remove All
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $90 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
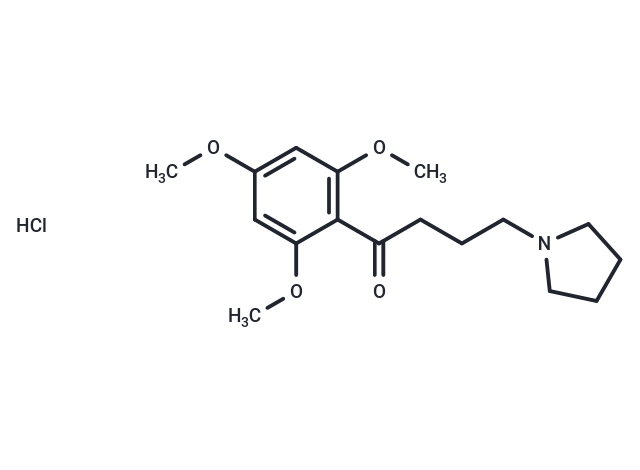
| Description | Buflomedil hydrochloride (Fonzylane), a vasodilator, is used in therapy of claudication or the symptoms of the peripheral arterial disease. |
| In vitro | Buflomedil enhances intracellular cAMP levels in human keratinocytes, either secondary to adenyl-cyclase stimulation (BC) or phosphodiesterase inhibition (PTX). Buflomedil diminishes release of TPA-induced TNF-alpha and IL-8 in keratinocytes; in the case of IL-8, this inhibition may occur to transcriptional level. At the micromolar level, Buflomedil notably inhibits epinephrine-induced aggregation. Buflomedil leads to a weak inhibition of collagen- and ADP-induced aggregation. Buflomedil inhibits grainy secretion and the interaction of fibrinogen with its receptor on platelet. the capillary perfusion is improved by Buflomedil hypochloride in such related situations, evoking a possible effect upon neutrophils. Buflomedil Completely inhibits adhesion of histamine related neutrophil (flow system) and partially inhibits adhesion after IL-1-4 hours (flow and stable systems). Buflomedil lowers the hypoxia-induced neutrophil adhesion and expression of P-selectin at the surface of endothelial cells. |
| Alias | Buflomedil HCl, Fonzylane, Loftyl |
| Molecular Weight | 343.85 |
| Formula | C17H26ClNO4 |
| Cas No. | 35543-24-9 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 7 mg/mL (20.35 mM) H2O: 63 mg/mL (183.2 mM) DMSO: 50 mg/mL (145.41 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.