Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

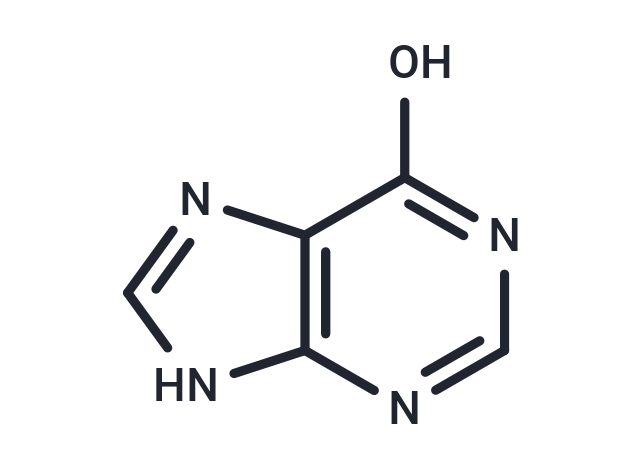
Hypoxanthine (Purin-6-ol), also known as purine-6-ol or Hyp. Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative and a reaction intermediate in the metabolism of adenosine and in the formation of nucleic acids by the nucleotide salvage pathway. Under normal circumstances hypoxanthine is readily converted to uric acid.hypoxanthine is first oxidized to xanthine, which is further oxidized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $37 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $113 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $163 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | Hypoxanthine (Purin-6-ol), also known as purine-6-ol or Hyp. Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative and a reaction intermediate in the metabolism of adenosine and in the formation of nucleic acids by the nucleotide salvage pathway. Under normal circumstances hypoxanthine is readily converted to uric acid.hypoxanthine is first oxidized to xanthine, which is further oxidized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase. |
| In vitro | Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids, where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in a certain cell, bacteria, and parasite cultures as a substrate and nitrogen source. [1] |
| In vivo | A linear increase of plasma hypoxanthine with duration of hypoxemia is found in pigs, and there is no difference between arterial and venous plasma. There are good correlations between hypoxanthine and lactate, base deficit and pH. Moreover, there is a direct relationship between survival time and an increase in plasma hypoxanthine. Survival time correlates negatively with the rate of hypoxanthine increase (r=-0.62). All animals die when hypoxanthine exceeds 125 pM/liter. The increase of hypoxanthine, thus, reflected the prognosis of acute hypoxia in contrast to base deficit[1]. |
| Alias | Sarkin, Sarcine, Purin-6-ol, 6-Hydroxypurine |
| Molecular Weight | 136.11 |
| Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Cas No. | 68-94-0 |
| Smiles | OC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.4295 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: Insoluble DMSO: 5 mg/mL (36.73 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.