- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
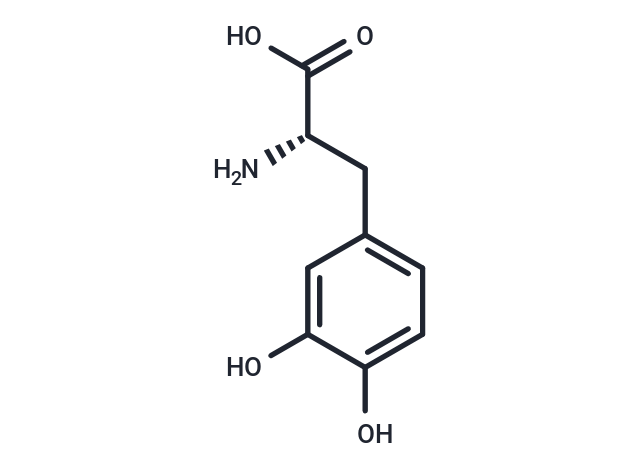
L-DOPA
Catalog No. T0848Cas No. 59-92-7
Alias Levodopa, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine
L-DOPA (Levodopa) is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. It is a prodrug converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. In the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine, stimulating dopaminergic receptors and compensating for depleted endogenous dopamine in Parkinson's disease. To ensure adequate concentrations reach the central nervous system, levodopa is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing peripheral decarboxylation and increasing CNS dopamine delivery.
L-DOPA
Catalog No. T0848Alias Levodopa, 3,4-DihydroxyphenylalanineCas No. 59-92-7
L-DOPA (Levodopa) is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. It is a prodrug converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. In the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine, stimulating dopaminergic receptors and compensating for depleted endogenous dopamine in Parkinson's disease. To ensure adequate concentrations reach the central nervous system, levodopa is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing peripheral decarboxylation and increasing CNS dopamine delivery.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $50 | In Stock |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Purity:99.93%
Contact us for more batch information
All TargetMol products are for research purposes only and cannot be used for human consumption. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use TargetMol products for any other purpose.Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | L-DOPA (Levodopa) is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. It is a prodrug converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. In the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine, stimulating dopaminergic receptors and compensating for depleted endogenous dopamine in Parkinson's disease. To ensure adequate concentrations reach the central nervous system, levodopa is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing peripheral decarboxylation and increasing CNS dopamine delivery. |
| In vitro | Levodopa produces at 25-200 μM concentrations a dose-dependent reduction of 3H-DA uptake in foetal rat midbrain cultures. Levodopa results in a decrease in the number of viable cells and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive neurones, plus disruption of the overall neuritic network. [1] Levodopa induces dyskinesia in the absence of dopamine by excessive inhibition of neurons of the putamen-globus pallidus (GPe) projection and subsequent disinhibition of the globus pallidus (GPe). Levodopa results in a decrease in cytochrome oxidase messenger RNA expression in the globus pallidus (GPi). [2] |
| In vivo | Levodopa elicits the development of a variety of abnormal movements in monkeys with parkinsonism induced by the neurotoxin MPTP. Levodopa administrations result in an ectopic induction of the dopamine D3receptor expression in the CdPu in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. [3] Levodopa (50 mg/kg) increases anandamide concentrations throughout thebasal ganglia via activation of dopamine D1/D2 receptors in intact rats. Levodopa produces increasingly severe oro-lingual involuntary movements which are attenuated by the cannabinoid agonist R(+)-WIN55,212-2 (1 mg/kg) in lesioned rats. [4] Levodopa administration reverses the up-regulation of D2 dopamine receptors seen in severely lesioned rats provided evidence that Levodopa reaches a biologically active concentration at the basal ganglia. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | Briefly, transfected HEK-293 cells, incubated in charcoal-treated Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium for 24 h, are washed once with Hanks' solution and resuspended in a buffer containing 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 250 mMsucrose, 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4. Cells are lysed by freezing in liquid nitrogen. Dehydrogenase activity is measured in a final volume of 20 μL containing the appropriate concentration of bile acid, 30 nCi of [3H]cortisol, and unlabeled cortisol to a final concentrations of 50 nM. The reaction is started by mixing cell lysate with the reaction mixture. Alternatively, endoplasmic reticulum microsomes are prepared from transfected HEK-293 cells and incubated with reaction mixture containing various concentrations of cortisol and CDCA. Incubation proceeded for 20 min, and the conversion of cortisol to cortisone is determined by thin layer chromatography (TLC). Because of the inaccuracy of the TLC method at low conversion rates and the end-product inhibition of 11βHSD2 at conversion rates higher than 60-70%, only conversion rates between 10 and 60% are considered for calculation. The inhibitory constant IC50 is evaluated using the curve-fitting program. Results are expressed as means±S.E. and consist of at least four independent measurements. |
| Alias | Levodopa, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| Molecular Weight | 197.19 |
| Formula | C9H11NO4 |
| Cas No. | 59-92-7 |
| Smiles | N[C@@H](Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.3075 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Insoluble H2O: 2.5 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Keywords
Related Tags: buy L-DOPA | purchase L-DOPA | L-DOPA cost | order L-DOPA | L-DOPA chemical structure | L-DOPA in vivo | L-DOPA in vitro | L-DOPA formula | L-DOPA molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



