Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

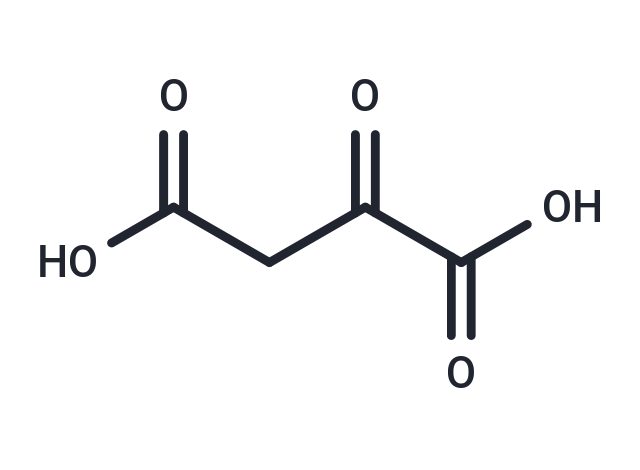
Oxaloacetic acid, also known as oxosuccinic acid or oxalacetic acid, is a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid appearing as an intermediate of the citric acid cycle. In vivo, oxaloacetate (the ionized form of oxaloacetic acid) is formed by the oxidation of L-malate, catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, and reacts with Acetyl-CoA to form citrate, catalyzed by citrate synthase.(wikipedia) A class of ketodicarboxylic acids derived from oxalic acid. Oxaloacetic acid is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle and is converted to aspartic acidD by a transamination reaction.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock |
| Description | Oxaloacetic acid, also known as oxosuccinic acid or oxalacetic acid, is a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid appearing as an intermediate of the citric acid cycle. In vivo, oxaloacetate (the ionized form of oxaloacetic acid) is formed by the oxidation of L-mal |
| Molecular Weight | 132.07 |
| Formula | C4H4O5 |
| Cas No. | 328-42-7 |
| Smiles | OC(=O)CC(=O)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.3067 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (340.73 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.