Shopping Cart
- Remove All
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 g | $39 | In Stock |
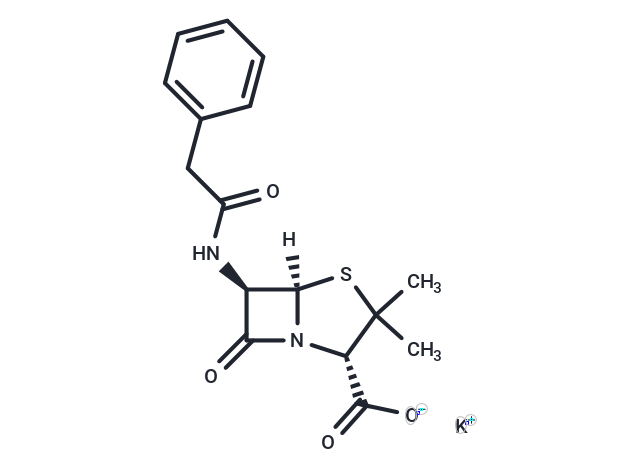
| Description | Penicillin G potassium (Benzylpenicillin potassium) is the potassium salt form of penicillin G, a broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic. |
| In vivo | Potassium penicillin G administered in drinking water is effective in reducing mortality associated with S. suis infection and reducing tonsillar carriage of S. suis that may lead to disease and be a source of pig-to-pig transmission of infection[1]. |
| Animal Research | Fresh stock solution was prepared twice daily by an individual who was not involved with assessment of the study pigs. The test article was administered via the drinking water for 5 d over 2 periods of treatment. The first treatment period commenced on the day of weaning, when the pigs were moved into the nursery barns (Day 1) and ended on Day 5. The second treatment period began on Day 21 and ended on Day 25. The Control group did not receive treatment[1]. |
| Alias | Benzylpenicillin potassium |
| Molecular Weight | 372.48 |
| Formula | C16H17KN2O4S |
| Cas No. | 113-98-4 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 200 mg/mL (536.9 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.